|
|
|
In the United States, there is a birth every 8 seconds, according to the U.S. Census Bureau's Population Clock.
The first war in which wide-scale use of anesthetics occurred was the Civil War, and 80% of all wounds were in the extremities.
IgA antibodies protect body surfaces exposed to outside foreign substances. IgG antibodies are found in all body fluids. IgM antibodies are the first type of antibody made in response to an infection. IgE antibody levels are often high in people with allergies. IgD antibodies are found in tissues lining the abdomen and chest.
Your chance of developing a kidney stone is 1 in 10. In recent years, approximately 3.7 million people in the United States were diagnosed with a kidney disease.
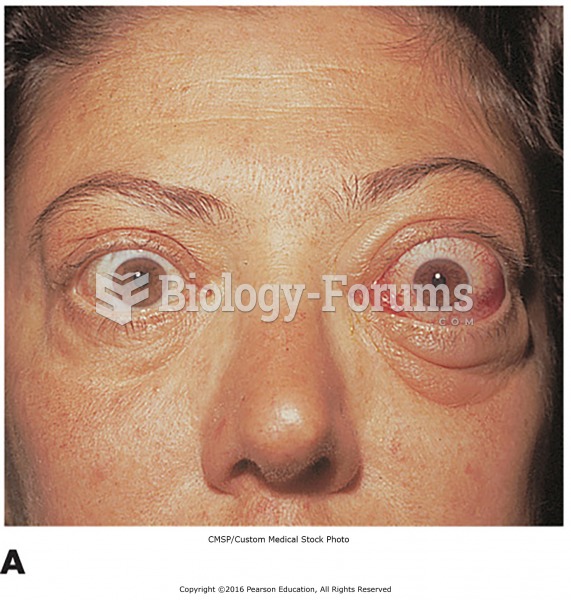
Hyperthyroidism leads to an increased rate of metabolism and affects about 1% of women but only 0.1% of men. For most people, this increased metabolic rate causes the thyroid gland to become enlarged (known as a goiter).