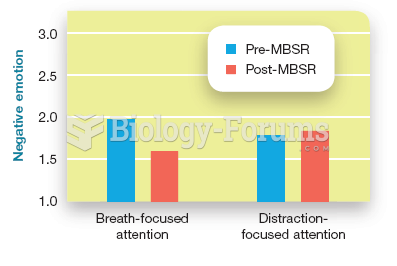
|
|
|
Nearly 31 million adults in America have a total cholesterol level that is more than 240 mg per dL.
Your skin wrinkles if you stay in the bathtub a long time because the outermost layer of skin (which consists of dead keratin) swells when it absorbs water. It is tightly attached to the skin below it, so it compensates for the increased area by wrinkling. This happens to the hands and feet because they have the thickest layer of dead keratin cells.
It is widely believed that giving a daily oral dose of aspirin to heart attack patients improves their chances of survival because the aspirin blocks the formation of new blood clots.
Asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the world. Most children who develop asthma have symptoms before they are 5 years old.
Tobacco depletes the body of vitamins A, C, and E, which can result in any of the following: dry hair, dry skin, dry eyes, poor growth, night blindness, abscesses, insomnia, fatigue, reproductive system problems, sinusitis, pneumonia, frequent respiratory problems, skin disorders, weight loss, rickets, osteomalacia, nervousness, muscle spasms, leg cramps, extremity numbness, bone malformations, decayed teeth, difficulty in walking, irritability, restlessness, profuse sweating, increased uric acid (gout), joint damage, damaged red blood cells, destruction of nerves, infertility, miscarriage, and many types of cancer.