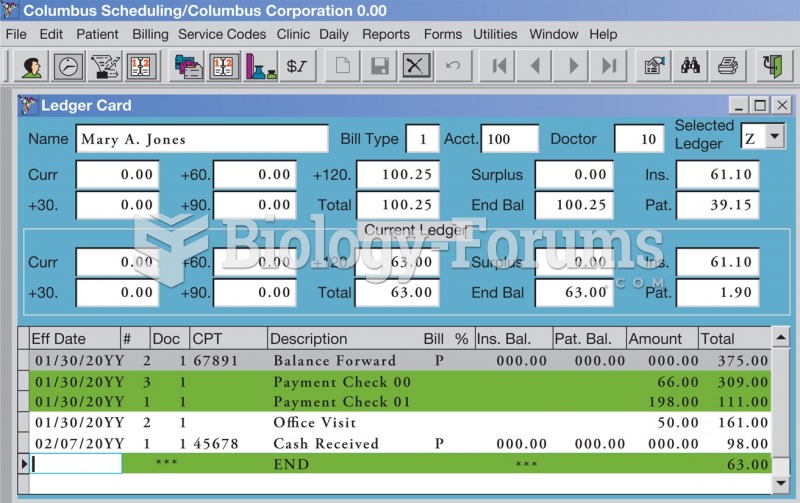
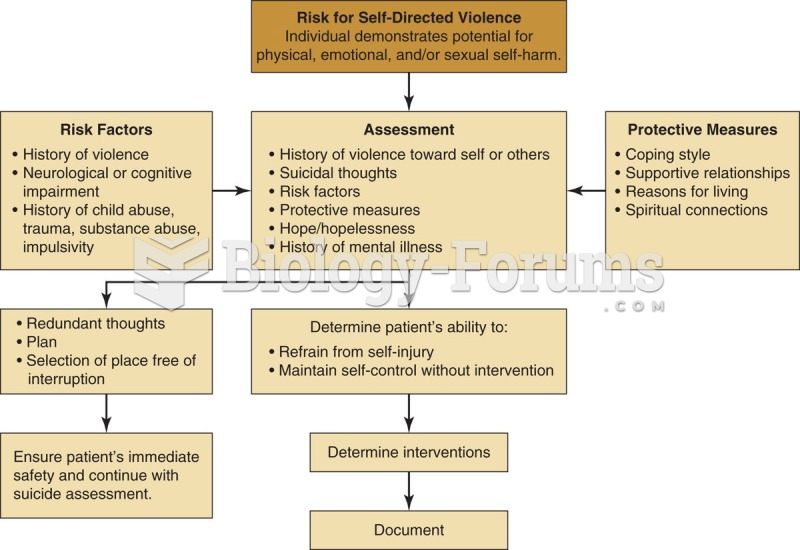
Answer to Question 1
B
The patient must monitor neurovascular status, paying particular attention to blueness or paleness of the nails, pain, a feeling of tightness, numbness, or a tingling sensation. Caution the patient against drying a wet cast with a hair dryer; this can cause plaster to crack or the skin underneath to be damaged. The patient should avoid sticking objects down or into the cast to scratch because these objects can cause breaks in underlying skin and subsequent infection. Inform the patient to inspect the cast and petal rough edges to reduce the risk of trauma to underlying skin and the need for cast changes. Small pieces (petals) of adhesive tape 2.5 to 5.0 cm (1 to 2 inches) are cut and taped smoothly over the edge of the cast.
Answer to Question 2
C
Encourage the patient to swallow by giving small sips of water or ice chips. Advance the tube as the patient swallows. Rotate the tube 180 degrees while inserting. Swallowing facilitates passage of the tube past the oropharynx. Position the patient sitting with the head of the bed elevated at least 30 degrees. If the patient is comatose, place him in semi-Fowler's position with the head propped forward using a pillow. If the patient is forced to lie supine, place him in reverse Trendelenburg's position. This reduces the risk for pulmonary aspiration in the event that the patient should vomit. Apply water-soluble lubricant. The tip of the tube must reach the stomach. Measure the distance from the tip of the nose to the earlobe to the xiphoid process of the sternum. Add 20 to 30 cm (8 to 12 inches) for a nasoenteric tube.