|
|
|
Though methadone is often used to treat dependency on other opioids, the drug itself can be abused. Crushing or snorting methadone can achieve the opiate "rush" desired by addicts. Improper use such as these can lead to a dangerous dependency on methadone. This drug now accounts for nearly one-third of opioid-related deaths.
Vital signs (blood pressure, temperature, pulse rate, respiration rate) should be taken before any drug administration. Patients should be informed not to use tobacco or caffeine at least 30 minutes before their appointment.
Patients who have undergone chemotherapy for the treatment of cancer often complain of a lack of mental focus; memory loss; and a general diminution in abilities such as multitasking, attention span, and general mental agility.
Earwax has antimicrobial properties that reduce the viability of bacteria and fungus in the human ear.
The use of salicylates dates back 2,500 years to Hippocrates’s recommendation of willow bark (from which a salicylate is derived) as an aid to the pains of childbirth. However, overdosage of salicylates can harm body fluids, electrolytes, the CNS, the GI tract, the ears, the lungs, the blood, the liver, and the kidneys and cause coma or death.
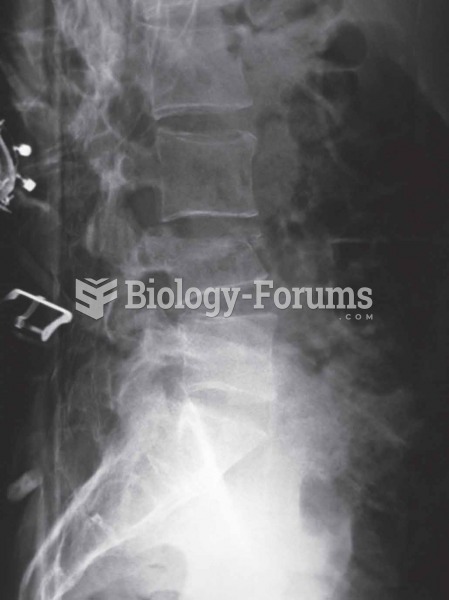 Vertebral compression Fractures of the spine (vertebra) can cause severe ”band-like” pain that radia
Vertebral compression Fractures of the spine (vertebra) can cause severe ”band-like” pain that radia
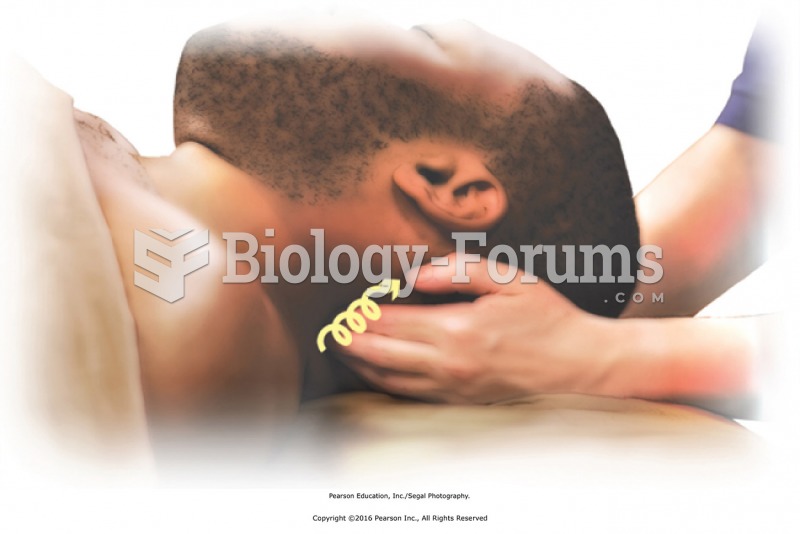 Apply circular friction to the left side of the neck along cervical muscles with the fingertips of ...
Apply circular friction to the left side of the neck along cervical muscles with the fingertips of ...