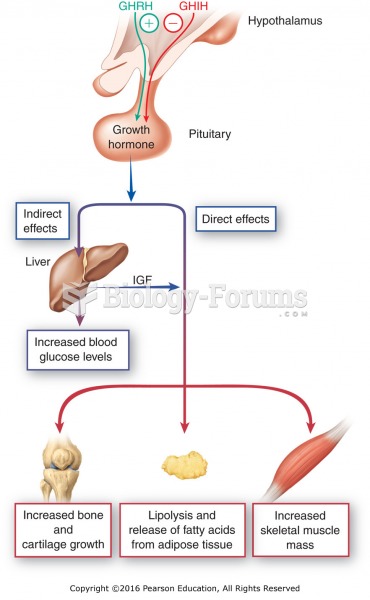
|
|
|
The training of an anesthesiologist typically requires four years of college, 4 years of medical school, 1 year of internship, and 3 years of residency.
Children with strabismus (crossed eyes) can be treated. They are not able to outgrow this condition on their own, but with help, it can be more easily corrected at a younger age. It is important for infants to have eye examinations as early as possible in their development and then another at age 2 years.
One way to reduce acid reflux is to lose two or three pounds. Most people lose weight in the belly area first when they increase exercise, meaning that heartburn can be reduced quickly by this method.
Immunoglobulin injections may give short-term protection against, or reduce severity of certain diseases. They help people who have an inherited problem making their own antibodies, or those who are having certain types of cancer treatments.
Malaria mortality rates are falling. Increased malaria prevention and control measures have greatly improved these rates. Since 2000, malaria mortality rates have fallen globally by 60% among all age groups, and by 65% among children under age 5.
 A whale off Australia on the spring migration, feeding on krill by turning on its side and propellin
A whale off Australia on the spring migration, feeding on krill by turning on its side and propellin
 Two-handed kneading on the upper leg. Apply kneading to medial, posterior, and lateral muscles of ...
Two-handed kneading on the upper leg. Apply kneading to medial, posterior, and lateral muscles of ...