This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Essential fatty acids have been shown to be effective against ulcers, asthma, dental cavities, and skin disorders such as acne.
Did you know?
The FDA recognizes 118 routes of administration.
Did you know?
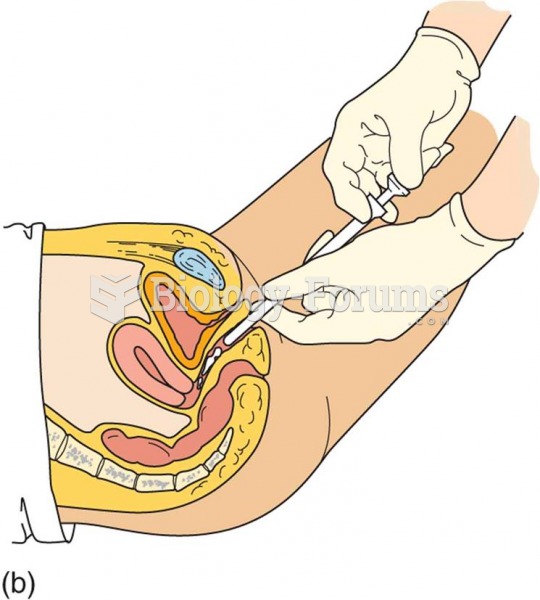
Patients who cannot swallow may receive nutrition via a parenteral route—usually, a catheter is inserted through the chest into a large vein going into the heart.
Did you know?
A good example of polar molecules can be understood when trying to make a cake. If water and oil are required, they will not mix together. If you put them into a measuring cup, the oil will rise to the top while the water remains on the bottom.
Did you know?
Less than one of every three adults with high LDL cholesterol has the condition under control. Only 48.1% with the condition are being treated for it.