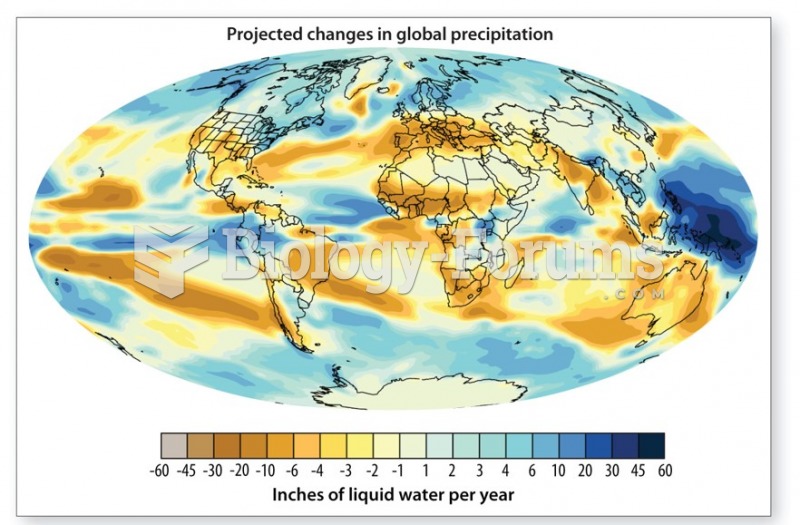
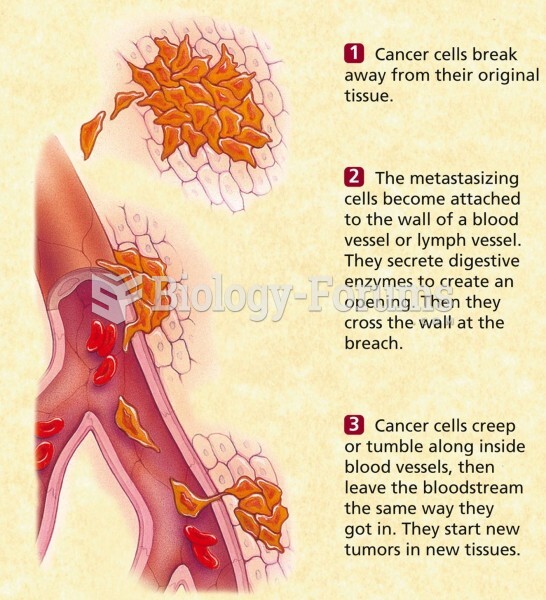
|
|
|
Did you know?
Amoebae are the simplest type of protozoans, and are characterized by a feeding and dividing trophozoite stage that moves by temporary extensions called pseudopodia or false feet.
Did you know?
The B-complex vitamins and vitamin C are not stored in the body and must be replaced each day.
Did you know?
There are approximately 3 million unintended pregnancies in the United States each year.
Did you know?
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.
Did you know?
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all women age 65 years of age or older should be screened with bone densitometry.