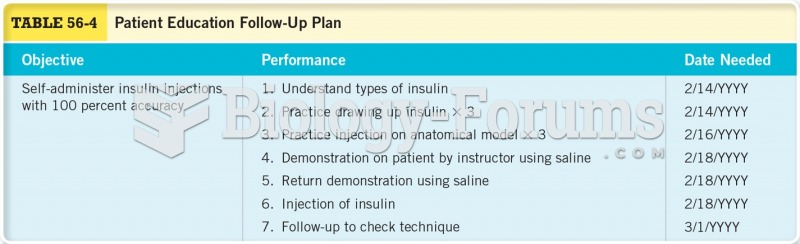
|
|
|
Did you know?
According to the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, lung disease is the third leading killer in the United States, responsible for one in seven deaths. It is the leading cause of death among infants under the age of one year.
Did you know?
There are over 65,000 known species of protozoa. About 10,000 species are parasitic.
Did you know?
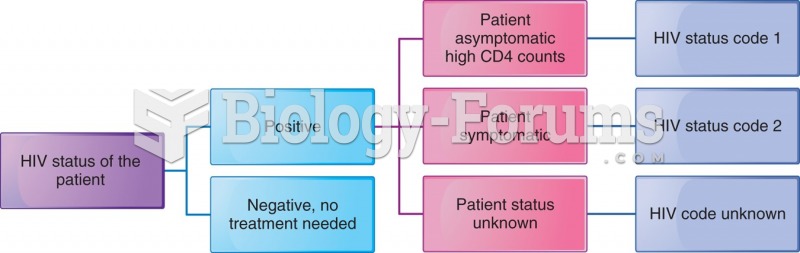
Today, nearly 8 out of 10 pregnant women living with HIV (about 1.1 million), receive antiretrovirals.
Did you know?
Oxytocin is recommended only for pregnancies that have a medical reason for inducing labor (such as eclampsia) and is not recommended for elective procedures or for making the birthing process more convenient.
Did you know?
There are 20 feet of blood vessels in each square inch of human skin.