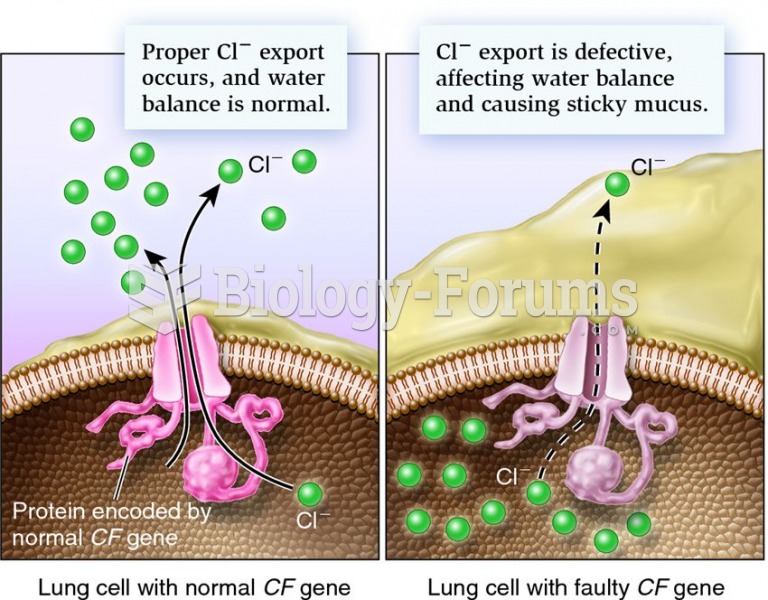
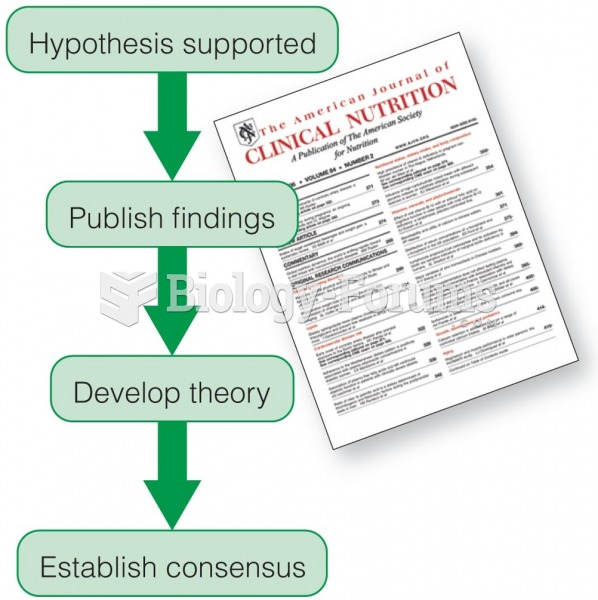
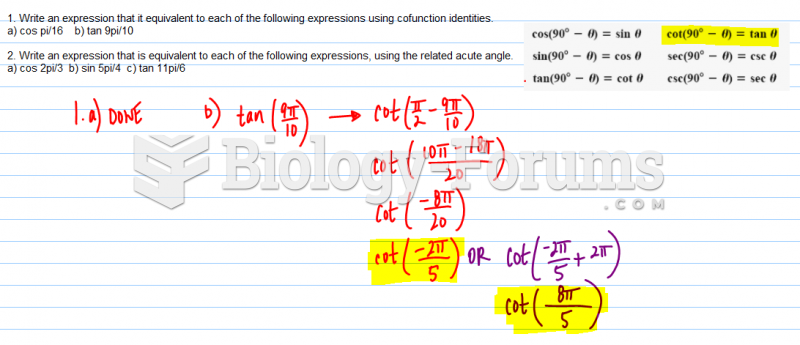
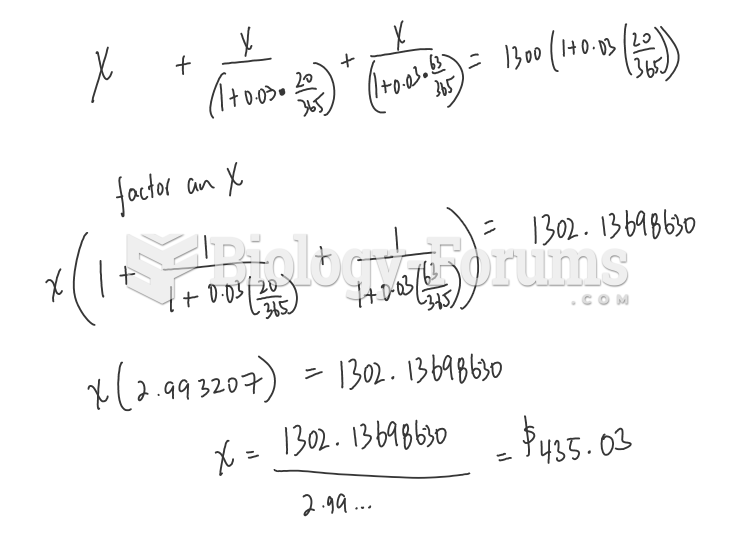
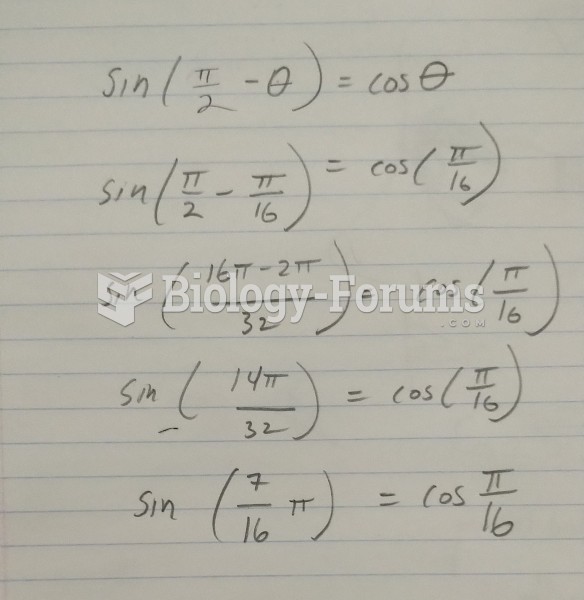- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
|
|
|
- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
As of mid-2016, 18.2 million people were receiving advanced retroviral therapy (ART) worldwide. This represents between 43–50% of the 34–39.8 million people living with HIV.
For pediatric patients, intravenous fluids are the most commonly cited products involved in medication errors that are reported to the USP.
Although puberty usually occurs in the early teenage years, the world's youngest parents were two Chinese children who had their first baby when they were 8 and 9 years of age.
If you could remove all of your skin, it would weigh up to 5 pounds.
Studies show that systolic blood pressure can be significantly lowered by taking statins. In fact, the higher the patient's baseline blood pressure, the greater the effect of statins on his or her blood pressure.