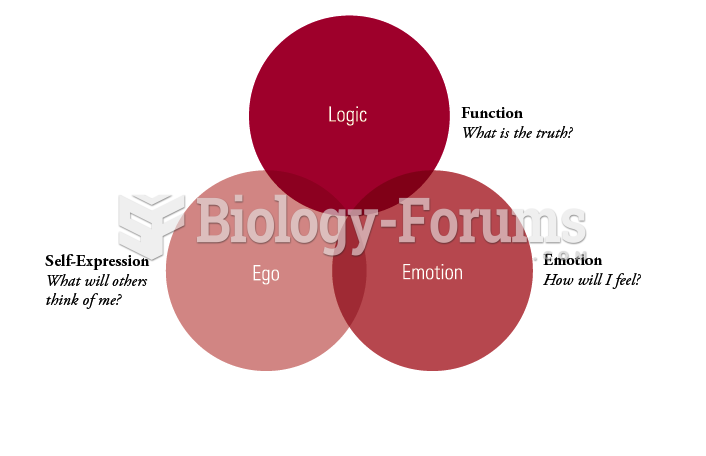
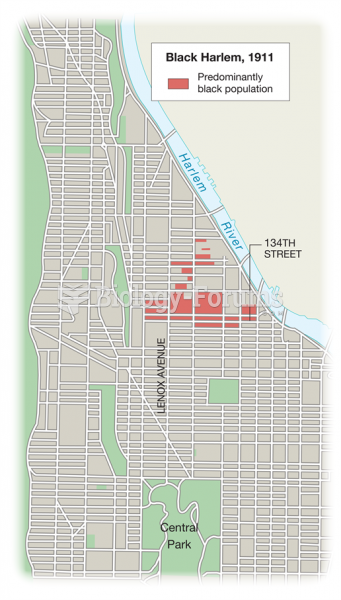
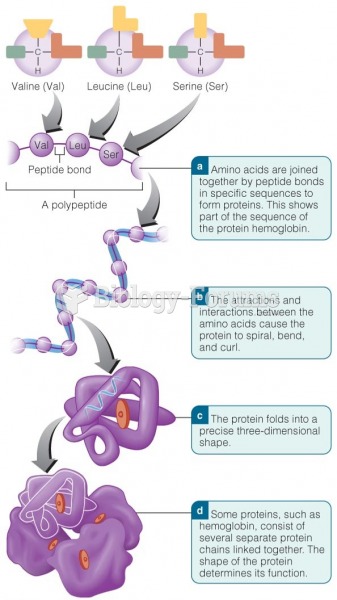
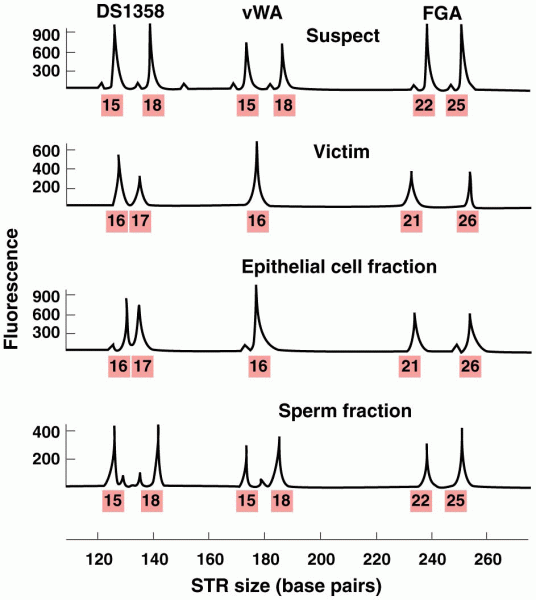
- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
|
|
|
- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
According to the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, lung disease is the third leading killer in the United States, responsible for one in seven deaths. It is the leading cause of death among infants under the age of one year.
The average human gut is home to perhaps 500 to 1,000 different species of bacteria.
ACTH levels are normally highest in the early morning (between 6 and 8 A.M.) and lowest in the evening (between 6 and 11 P.M.). Therefore, a doctor who suspects abnormal levels looks for low ACTH in the morning and high ACTH in the evening.
When intravenous medications are involved in adverse drug events, their harmful effects may occur more rapidly, and be more severe than errors with oral medications. This is due to the direct administration into the bloodstream.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.