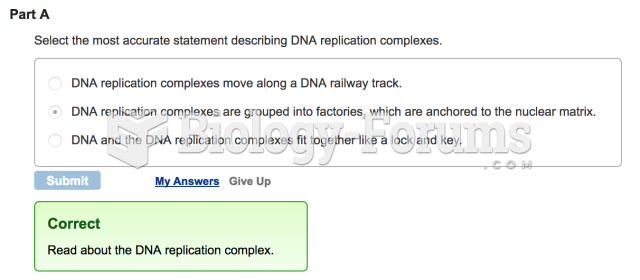
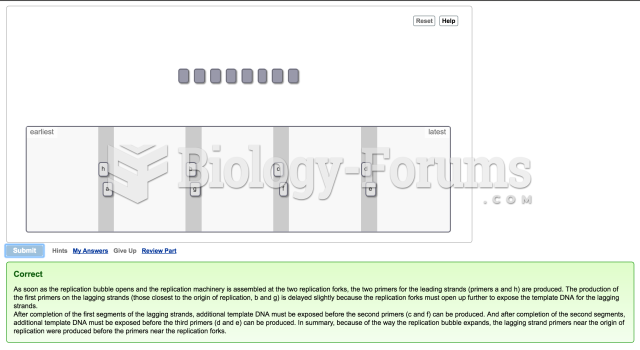
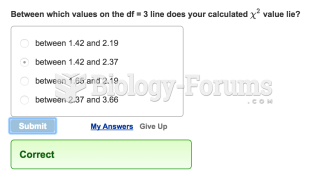
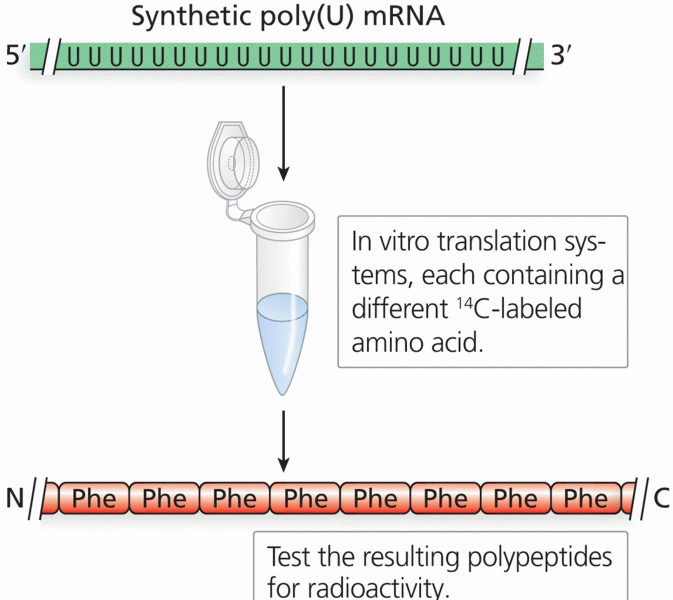
- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
Did you know?
Normal urine is sterile. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It is free of bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Did you know?
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
Did you know?
Bacteria have been found alive in a lake buried one half mile under ice in Antarctica.
Did you know?
Human stomach acid is strong enough to dissolve small pieces of metal such as razor blades or staples.
Did you know?
The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen in water (H2O) is 2:1.