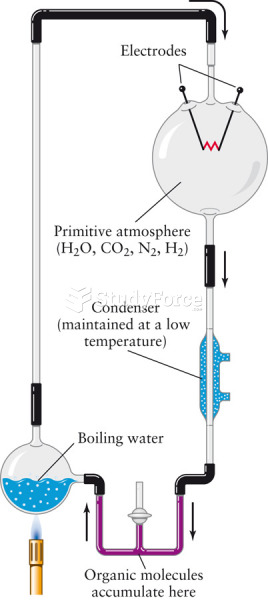
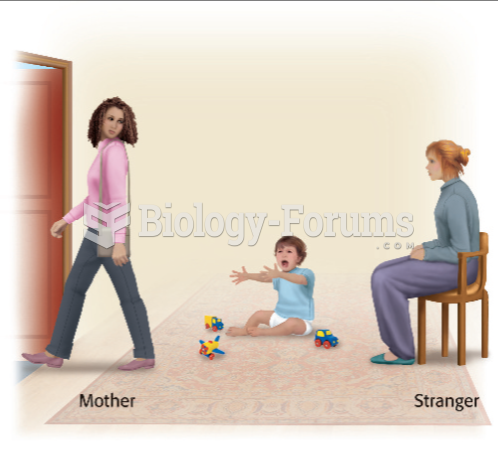
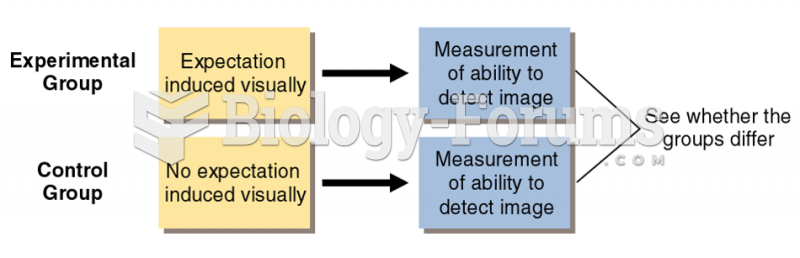
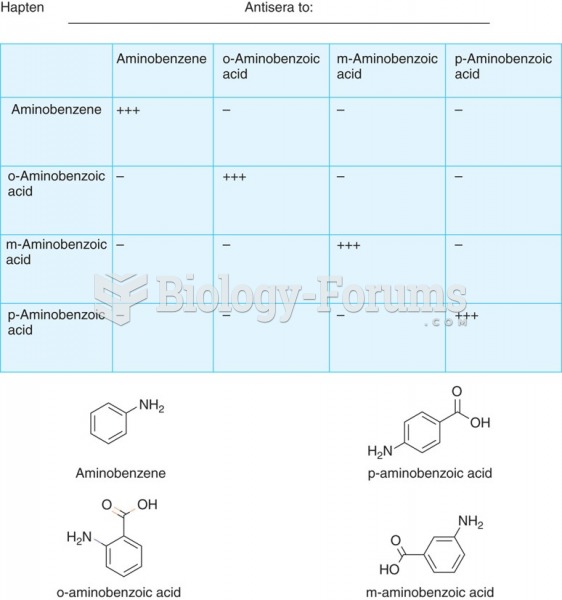
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
Did you know?
Walt Disney helped combat malaria by making an animated film in 1943 called The Winged Scourge. This short film starred the seven dwarfs and taught children that mosquitos transmit malaria, which is a very bad disease. It advocated the killing of mosquitos to stop the disease.
Did you know?
Between 1999 and 2012, American adults with high total cholesterol decreased from 18.3% to 12.9%
Did you know?
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.
Did you know?
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.