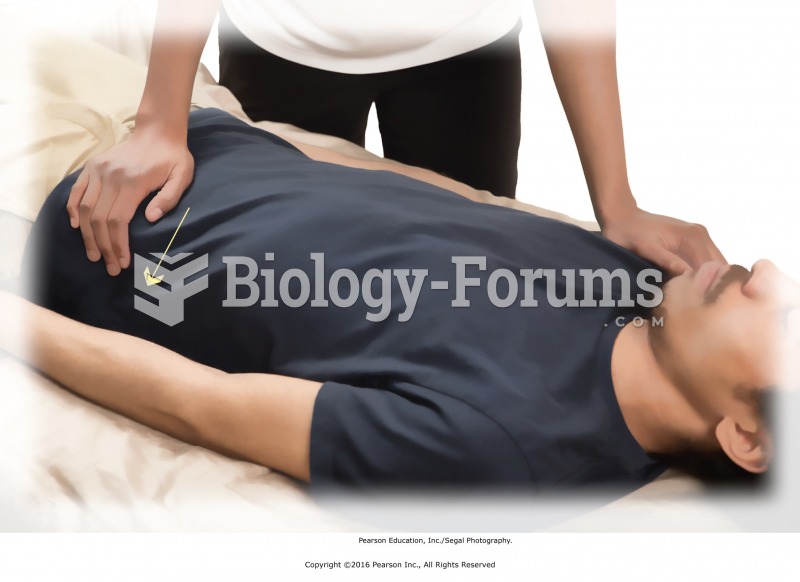
|
|
|
Most women experience menopause in their 50s. However, in 1994, an Italian woman gave birth to a baby boy when she was 61 years old.
Nearly all drugs pass into human breast milk. How often a drug is taken influences the amount of drug that will pass into the milk. Medications taken 30 to 60 minutes before breastfeeding are likely to be at peak blood levels when the baby is nursing.
The most common treatment options for addiction include psychotherapy, support groups, and individual counseling.
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.