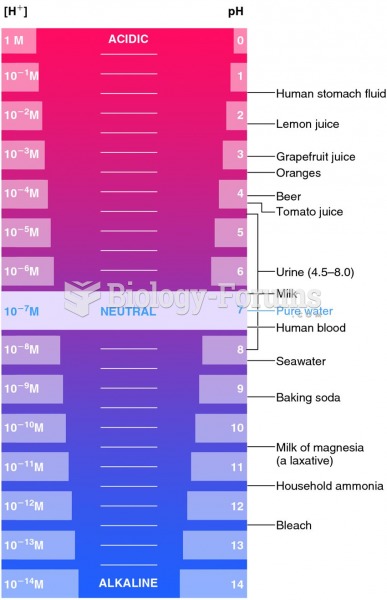
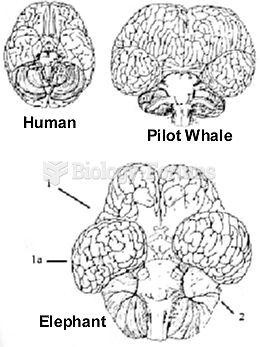
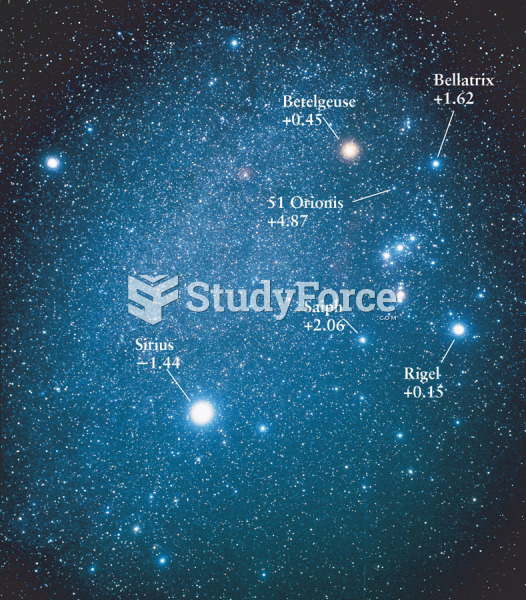
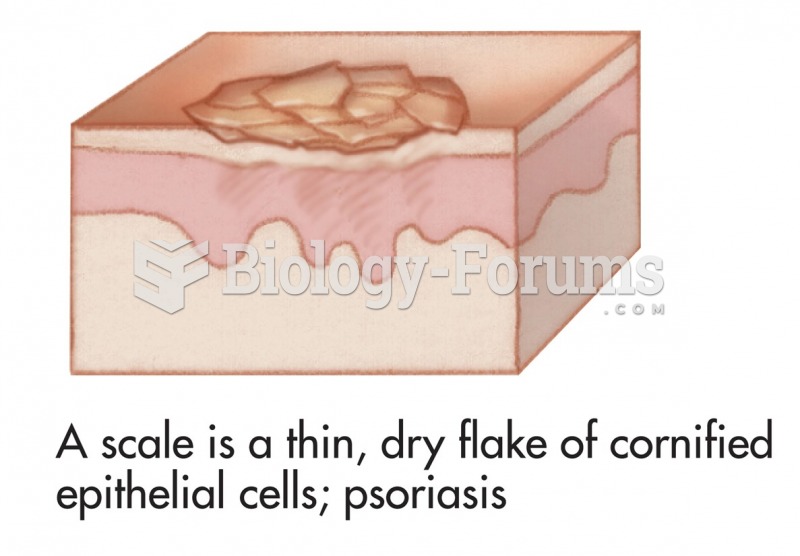
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
There are approximately 3 million unintended pregnancies in the United States each year.
Did you know?
The familiar sounds of your heart are made by the heart's valves as they open and close.
Did you know?
A seasonal flu vaccine is the best way to reduce the chances you will get seasonal influenza and spread it to others.
Did you know?
A headache when you wake up in the morning is indicative of sinusitis. Other symptoms of sinusitis can include fever, weakness, tiredness, a cough that may be more severe at night, and a runny nose or nasal congestion.
Did you know?
This year, an estimated 1.4 million Americans will have a new or recurrent heart attack.