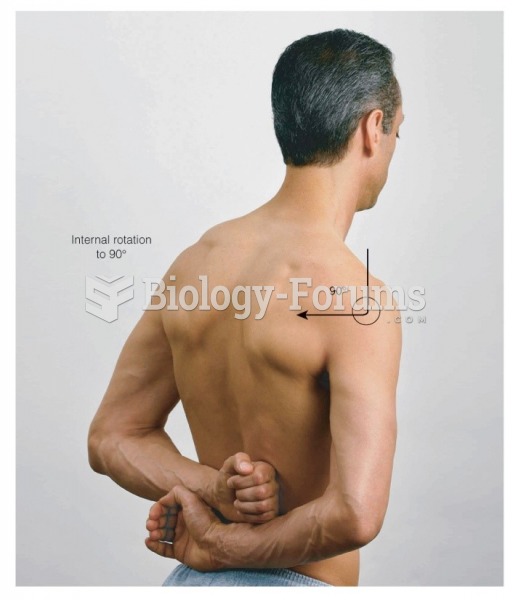
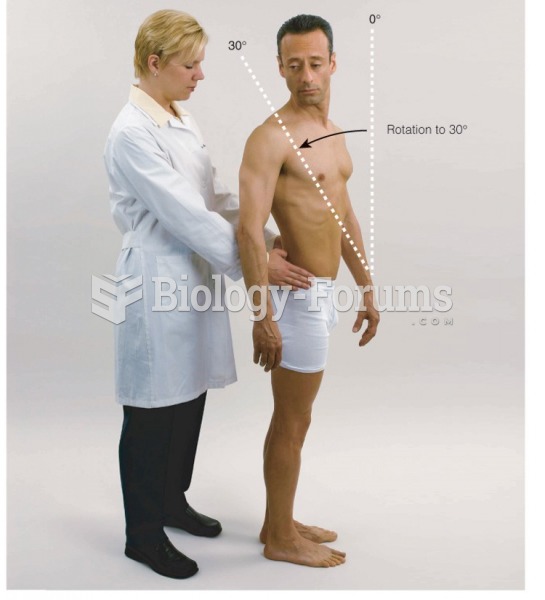
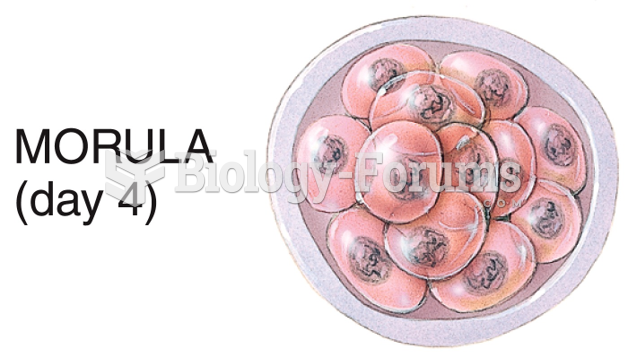
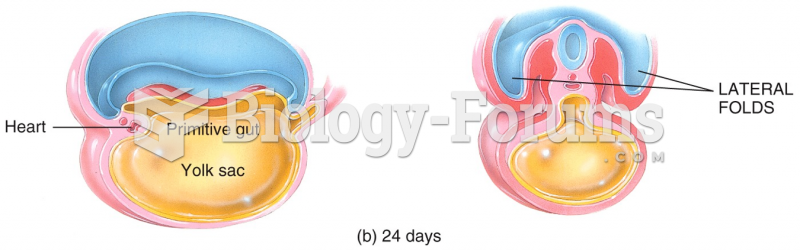
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
In 1844, Charles Goodyear obtained the first patent for a rubber condom.
Did you know?
Essential fatty acids have been shown to be effective against ulcers, asthma, dental cavities, and skin disorders such as acne.
Did you know?
Blood in the urine can be a sign of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problems.
Did you know?
There are major differences in the metabolism of morphine and the illegal drug heroin. Morphine mostly produces its CNS effects through m-receptors, and at k- and d-receptors. Heroin has a slight affinity for opiate receptors. Most of its actions are due to metabolism to active metabolites (6-acetylmorphine, morphine, and morphine-6-glucuronide).
Did you know?
The immune system needs 9.5 hours of sleep in total darkness to recharge completely.