|
|
|
Your skin wrinkles if you stay in the bathtub a long time because the outermost layer of skin (which consists of dead keratin) swells when it absorbs water. It is tightly attached to the skin below it, so it compensates for the increased area by wrinkling. This happens to the hands and feet because they have the thickest layer of dead keratin cells.
Approximately 70% of expectant mothers report experiencing some symptoms of morning sickness during the first trimester of pregnancy.
As the western states of America were settled, pioneers often had to drink rancid water from ponds and other sources. This often resulted in chronic diarrhea, causing many cases of dehydration and death that could have been avoided if clean water had been available.
Many of the drugs used by neuroscientists are derived from toxic plants and venomous animals (such as snakes, spiders, snails, and puffer fish).
The top five reasons that children stay home from school are as follows: colds, stomach flu (gastroenteritis), ear infection (otitis media), pink eye (conjunctivitis), and sore throat.
 Dred Scott and his wife and children are featured on the cover of Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspap
Dred Scott and his wife and children are featured on the cover of Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspap
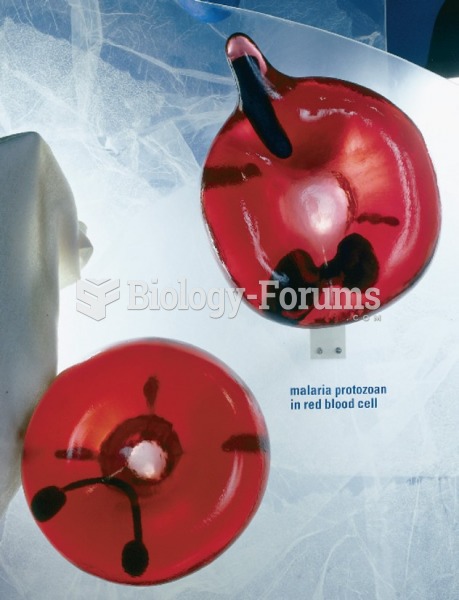 Model of malaria protozoa in a red blood cell. New parasites are produced and mature in the RBC, ...
Model of malaria protozoa in a red blood cell. New parasites are produced and mature in the RBC, ...