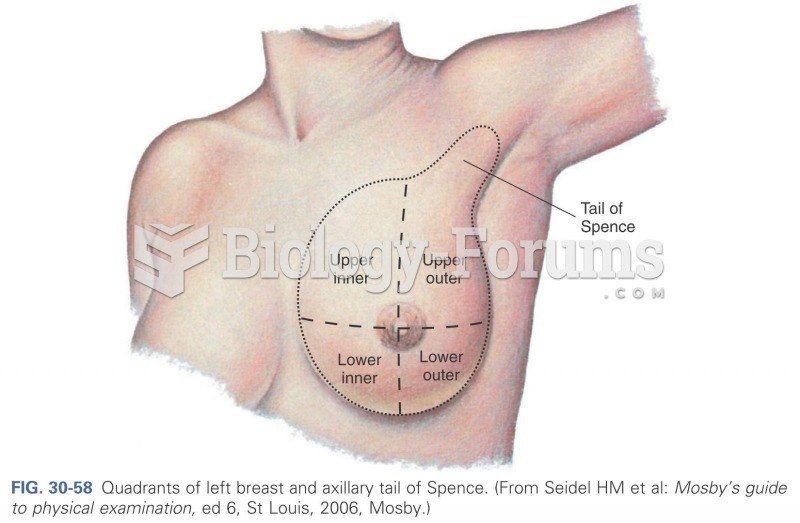
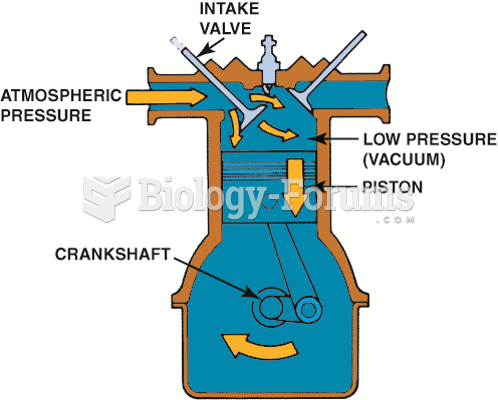
|
|
|
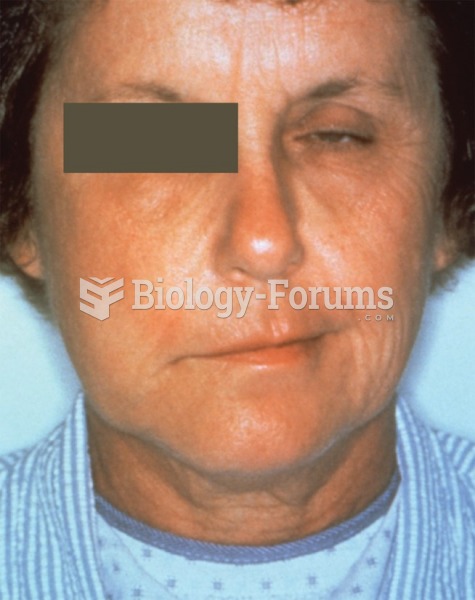
On average, someone in the United States has a stroke about every 40 seconds. This is about 795,000 people per year.
Illness; diuretics; laxative abuse; hot weather; exercise; sweating; caffeine; alcoholic beverages; starvation diets; inadequate carbohydrate consumption; and diets high in protein, salt, or fiber can cause people to become dehydrated.
The first monoclonal antibodies were made exclusively from mouse cells. Some are now fully human, which means they are likely to be safer and may be more effective than older monoclonal antibodies.
Automated pill dispensing systems have alarms to alert patients when the correct dosing time has arrived. Most systems work with many varieties of medications, so patients who are taking a variety of drugs can still be in control of their dose regimen.
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.
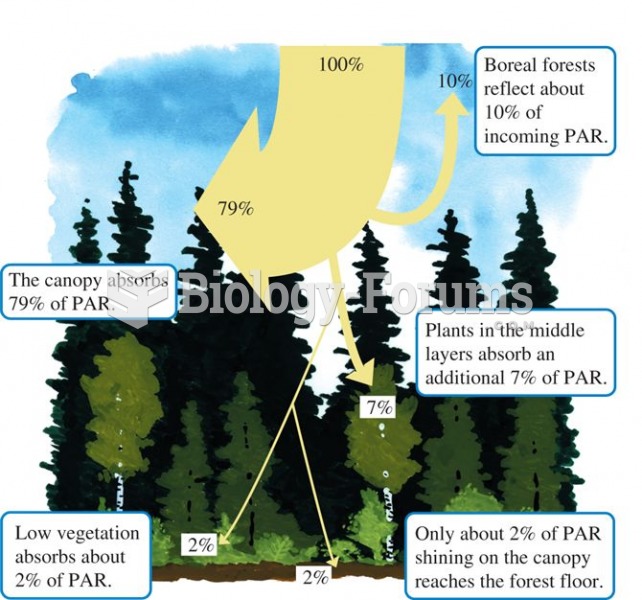 Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) diminishes substantially with passage through the canopy o
Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) diminishes substantially with passage through the canopy o
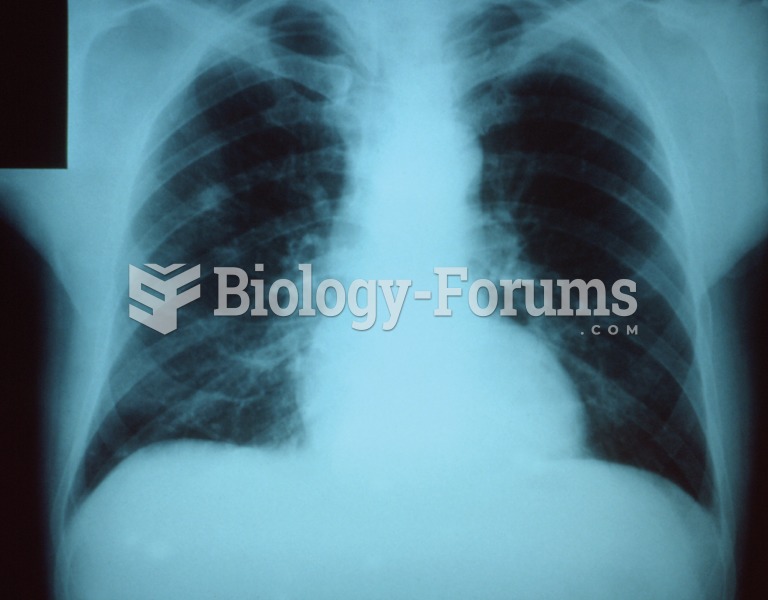 Pneumonia. This common lung inflammation may be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi and is often d
Pneumonia. This common lung inflammation may be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi and is often d