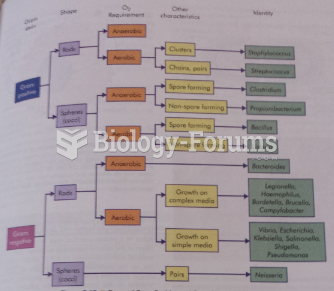
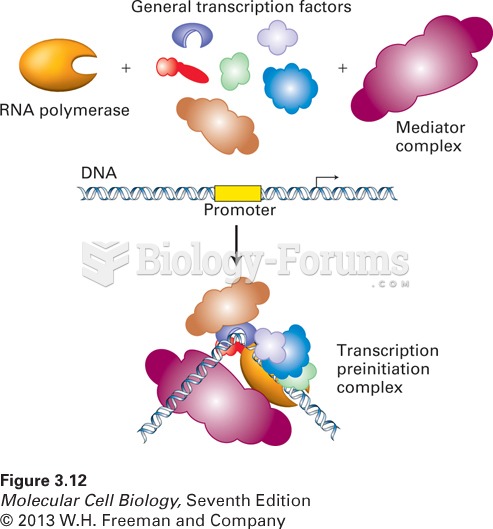
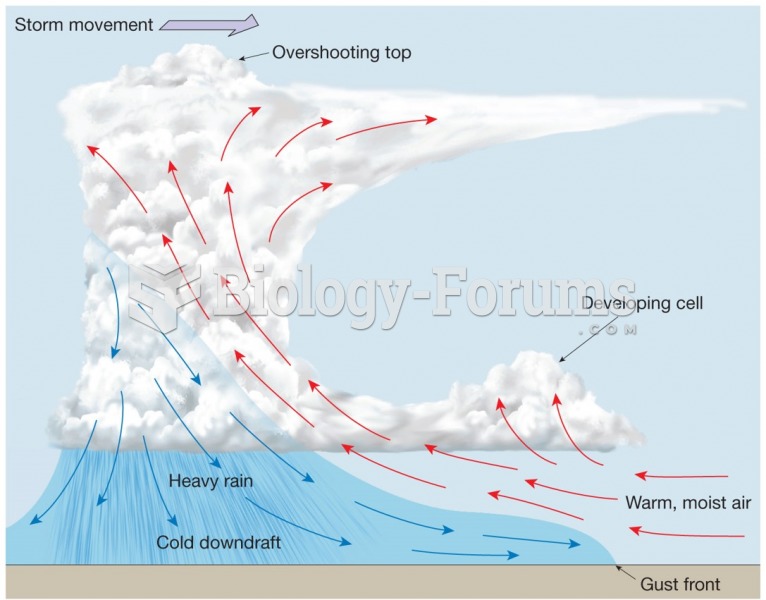
|
|
|
Not getting enough sleep can greatly weaken the immune system. Lack of sleep makes you more likely to catch a cold, or more difficult to fight off an infection.
Most women experience menopause in their 50s. However, in 1994, an Italian woman gave birth to a baby boy when she was 61 years old.
The most dangerous mercury compound, dimethyl mercury, is so toxic that even a few microliters spilled on the skin can cause death. Mercury has been shown to accumulate in higher amounts in the following types of fish than other types: swordfish, shark, mackerel, tilefish, crab, and tuna.
Patients should never assume they are being given the appropriate drugs. They should make sure they know which drugs are being prescribed, and always double-check that the drugs received match the prescription.
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.