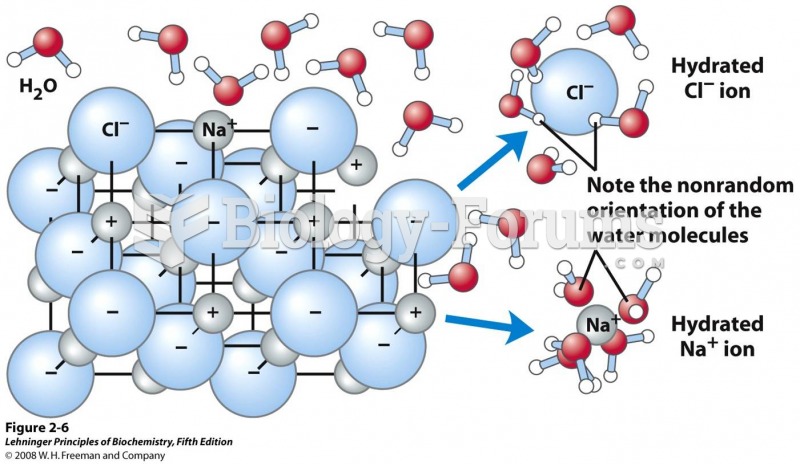
|
|
|
The first war in which wide-scale use of anesthetics occurred was the Civil War, and 80% of all wounds were in the extremities.
About one in five American adults and teenagers have had a genital herpes infection—and most of them don't know it. People with genital herpes have at least twice the risk of becoming infected with HIV if exposed to it than those people who do not have genital herpes.
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.
Colchicine is a highly poisonous alkaloid originally extracted from a type of saffron plant that is used mainly to treat gout.
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.