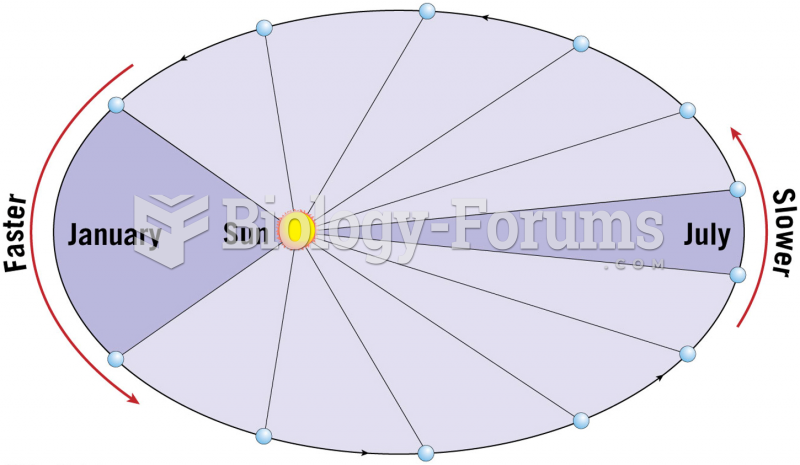
|
|
|
According to the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, lung disease is the third leading killer in the United States, responsible for one in seven deaths. It is the leading cause of death among infants under the age of one year.
In 1885, the Lloyd Manufacturing Company of Albany, New York, promoted and sold "Cocaine Toothache Drops" at 15 cents per bottle! In 1914, the Harrison Narcotic Act brought the sale and distribution of this drug under federal control.
About 100 new prescription or over-the-counter drugs come into the U.S. market every year.
Although puberty usually occurs in the early teenage years, the world's youngest parents were two Chinese children who had their first baby when they were 8 and 9 years of age.
Certain topical medications such as clotrimazole and betamethasone are not approved for use in children younger than 12 years of age. They must be used very cautiously, as directed by a doctor, to treat any child. Children have a much greater response to topical steroid medications.