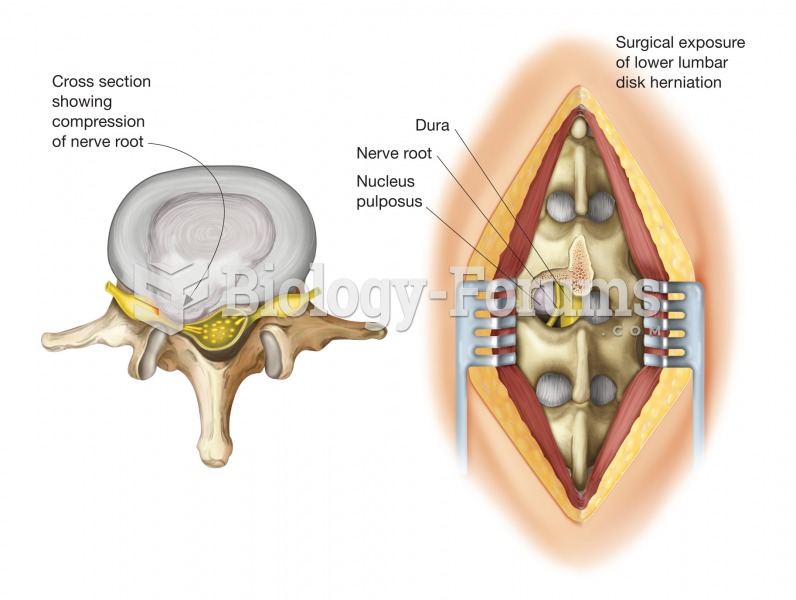
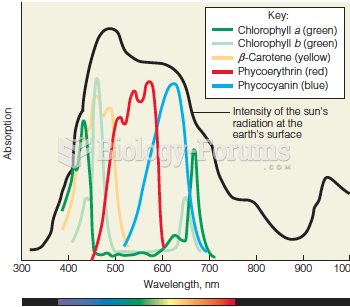
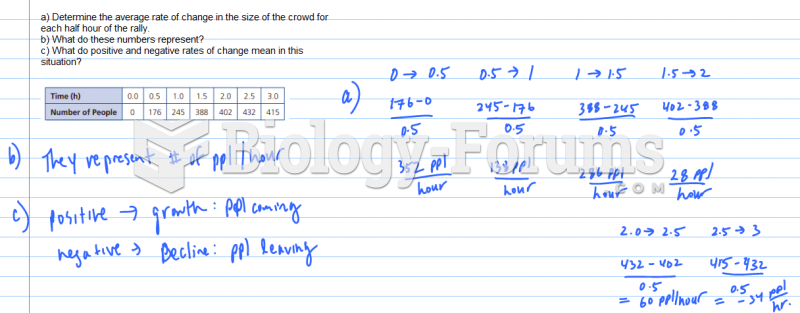
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Medication errors are more common among seriously ill patients than with those with minor conditions.
Did you know?
The types of cancer that alpha interferons are used to treat include hairy cell leukemia, melanoma, follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma.
Did you know?
If all the neurons in the human body were lined up, they would stretch more than 600 miles.
Did you know?
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system destroys its own healthy tissues. When this occurs, white blood cells cannot distinguish between pathogens and normal cells.
Did you know?
Multiple experimental evidences have confirmed that at the molecular level, cancer is caused by lesions in cellular DNA.