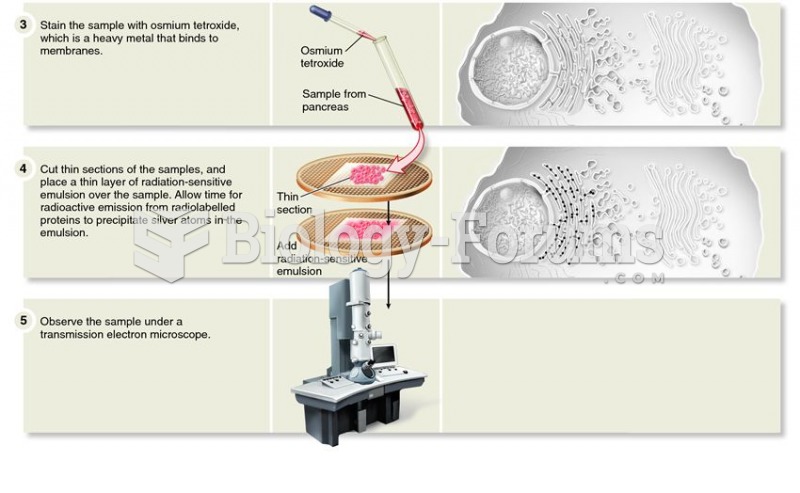
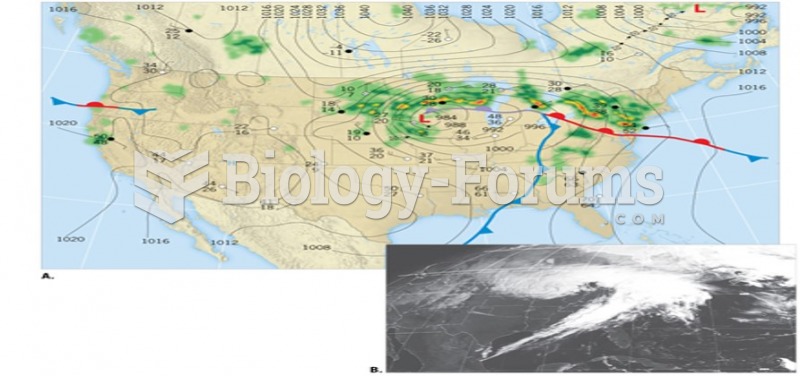
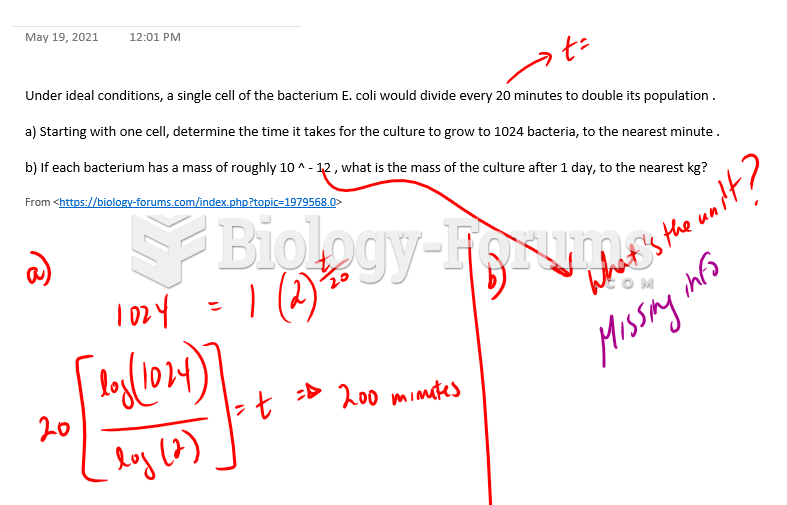
|
|
|
Addicts to opiates often avoid treatment because they are afraid of withdrawal. Though unpleasant, with proper management, withdrawal is rarely fatal and passes relatively quickly.
In 2012, nearly 24 milliion Americans, aged 12 and older, had abused an illicit drug, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
Patients should never assume they are being given the appropriate drugs. They should make sure they know which drugs are being prescribed, and always double-check that the drugs received match the prescription.
Malaria was not eliminated in the United States until 1951. The term eliminated means that no new cases arise in a country for 3 years.
Acute bronchitis is an inflammation of the breathing tubes (bronchi), which causes increased mucus production and other changes. It is usually caused by bacteria or viruses, can be serious in people who have pulmonary or cardiac diseases, and can lead to pneumonia.