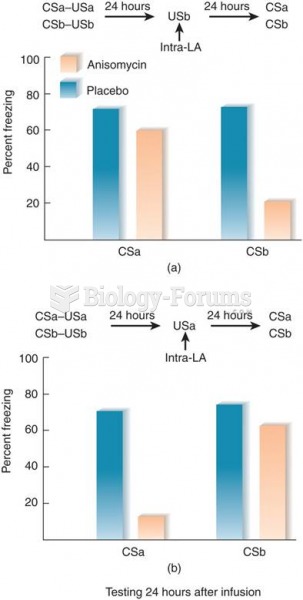
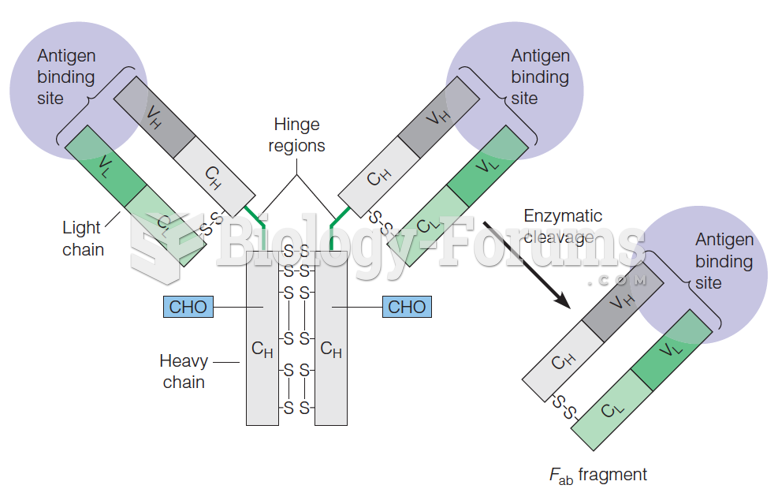
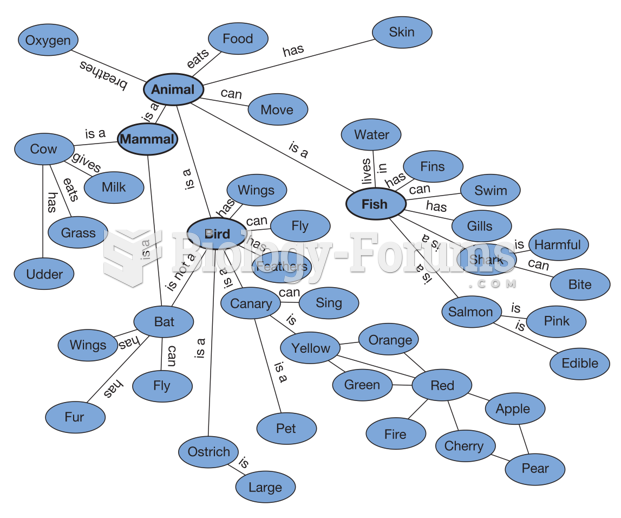
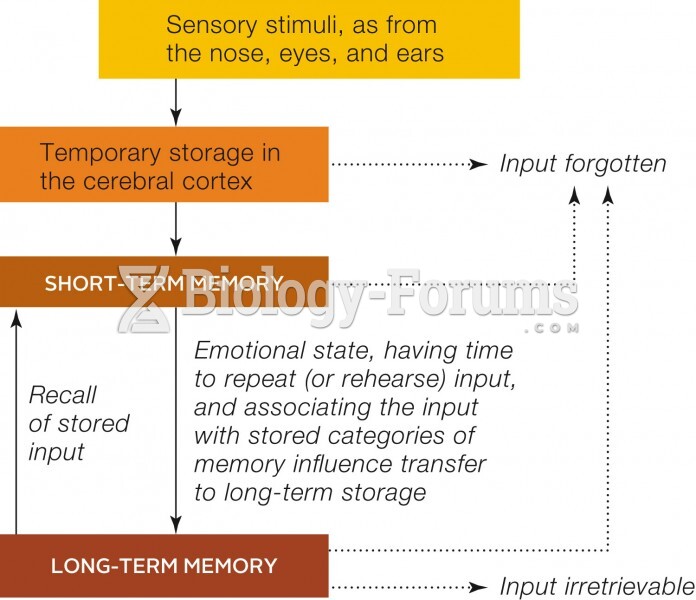
Answer to Question 1
Answer: The Atkinison-Shiffrin model is a multi-store model including sensory registers, short-term memory, and long-term memory. The model assumes a sequential order of processing. As a result, the short-term store is viewed as a link to long-term memory. Therefore, if the short-term store is impaired, then there should be a corresponding impairment with long-term memory. The Baddeley-Hitch does not include sensory registers or long-term memory. Instead, this model is a different conceptualization of short-term storage. In this view, short-term storage is more than a link to long-term storage. It is also a place where information is compared and manipulated. Thus, it is thought of as working memory. Working memory accounts for the processing of verbal information with the phonological loop and visual information with the visuospatial scratchpad. It also includes a control system in the central executive.
Answer to Question 2
Answer: The phonological similarity effect occurs when items simultaneously stored in working memory have to be serially recalled. Under these conditions, performance is significantly worse when the items to be maintained all sound the same. The word-length effect occurs when performance on a recall task is worse for long words than short words. The assumption is that longer words take longer to rehearse and, therefore, fewer items are rehearsed compared to short words. The unrehearsed words are then dropped from the phonological store. These tasks provide evidence for one component of working memory that maintains sound information (phonological store) and another component involved with articulatory processing (articulatory rehearsal).