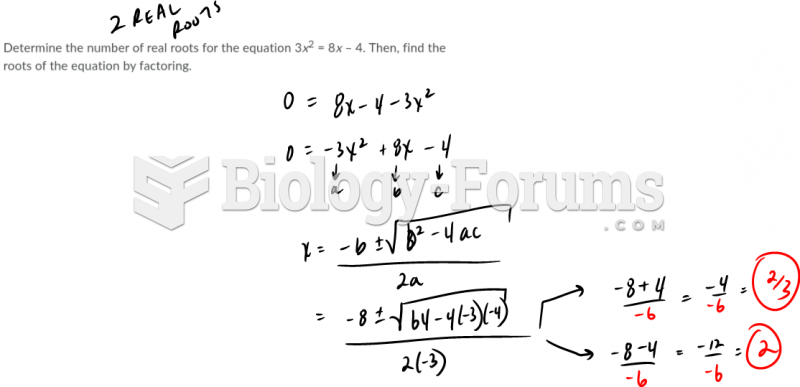
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Not getting enough sleep can greatly weaken the immune system. Lack of sleep makes you more likely to catch a cold, or more difficult to fight off an infection.
Did you know?
People with high total cholesterol have about two times the risk for heart disease as people with ideal levels.
Did you know?
A seasonal flu vaccine is the best way to reduce the chances you will get seasonal influenza and spread it to others.
Did you know?
In 2010, opiate painkllers, such as morphine, OxyContin®, and Vicodin®, were tied to almost 60% of drug overdose deaths.
Did you know?
Fungal nail infections account for up to 30% of all skin infections. They affect 5% of the general population—mostly people over the age of 70.