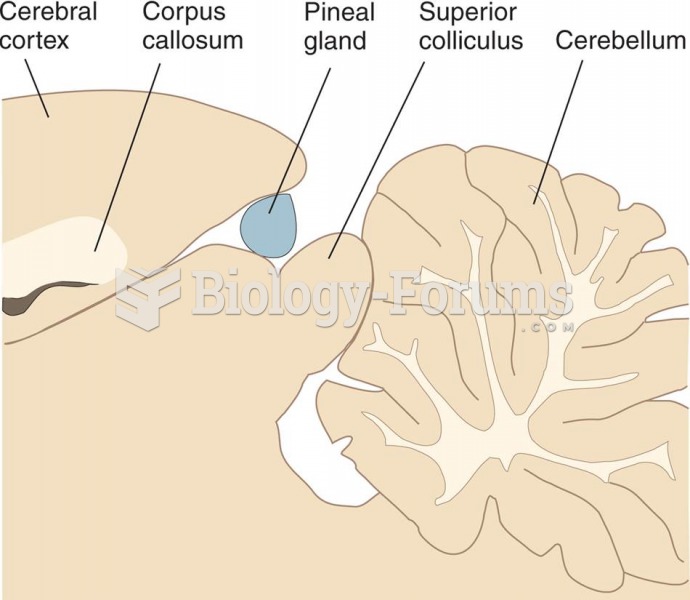
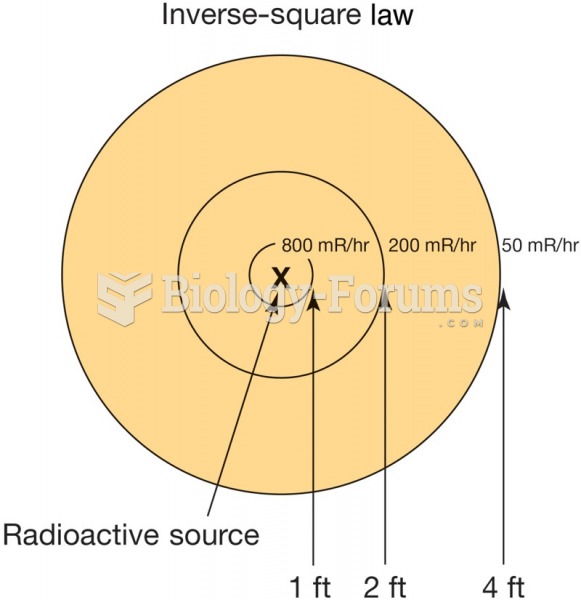
|
|
|
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.
Most fungi that pathogenically affect humans live in soil. If a person is not healthy, has an open wound, or is immunocompromised, a fungal infection can be very aggressive.
Long-term mental and physical effects from substance abuse include: paranoia, psychosis, immune deficiencies, and organ damage.
All adults should have their cholesterol levels checked once every 5 years. During 2009–2010, 69.4% of Americans age 20 and older reported having their cholesterol checked within the last five years.
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system destroys its own healthy tissues. When this occurs, white blood cells cannot distinguish between pathogens and normal cells.