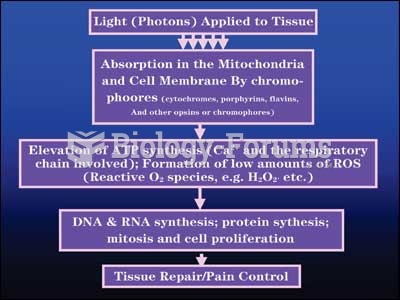
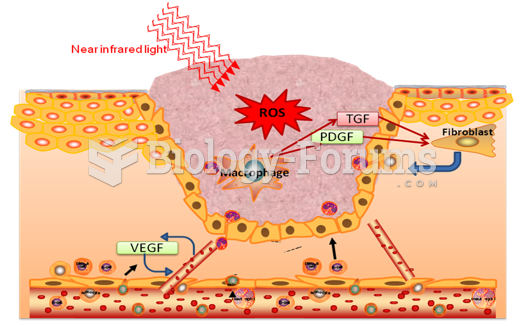
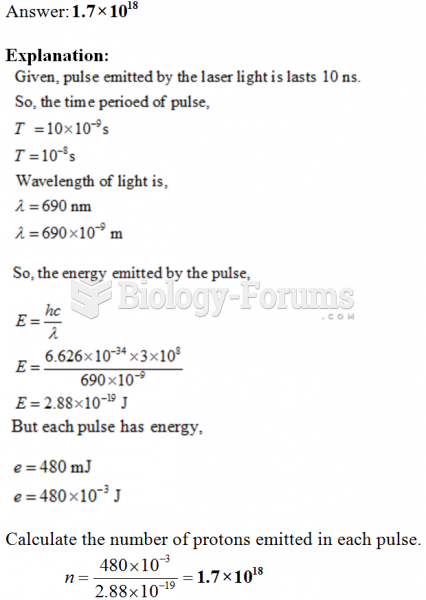This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Calcitonin is a naturally occurring hormone. In women who are at least 5 years beyond menopause, it slows bone loss and increases spinal bone density.
Did you know?
The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen in water (H2O) is 2:1.
Did you know?
Today, nearly 8 out of 10 pregnant women living with HIV (about 1.1 million), receive antiretrovirals.
Did you know?
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.
Did you know?
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).