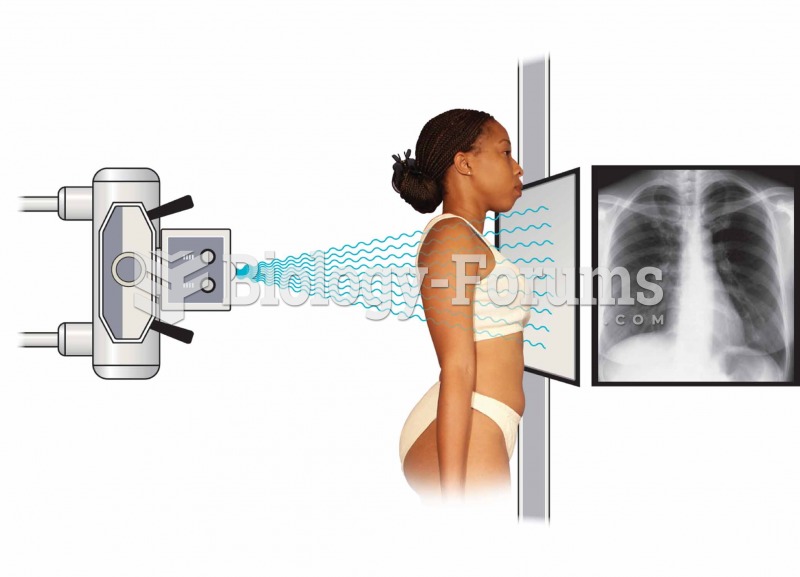
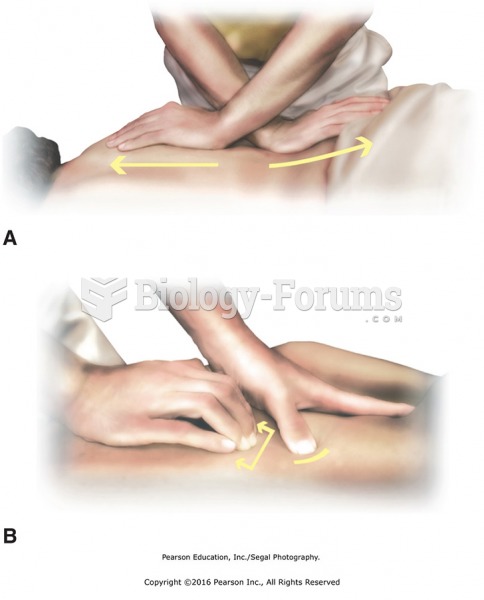
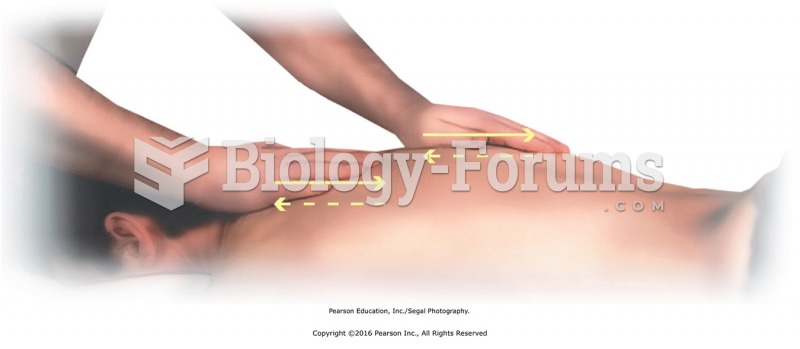
|
|
|
Serum cholesterol testing in adults is recommended every 1 to 5 years. People with diabetes and a family history of high cholesterol should be tested even more frequently.
The calories found in one piece of cherry cheesecake could light a 60-watt light bulb for 1.5 hours.
Multiple sclerosis is a condition wherein the body's nervous system is weakened by an autoimmune reaction that attacks the myelin sheaths of neurons.
Cutaneous mucormycosis is a rare fungal infection that has been fatal in at least 29% of cases, and in as many as 83% of cases, depending on the patient's health prior to infection. It has occurred often after natural disasters such as tornados, and early treatment is essential.
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.