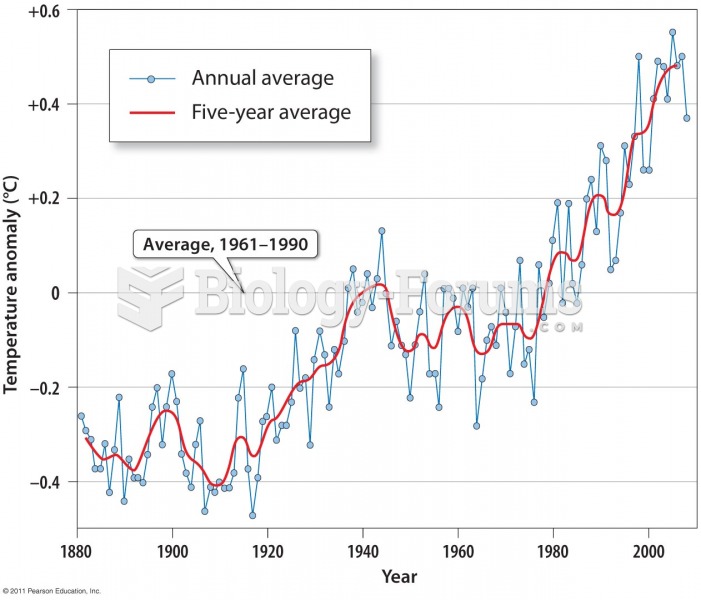
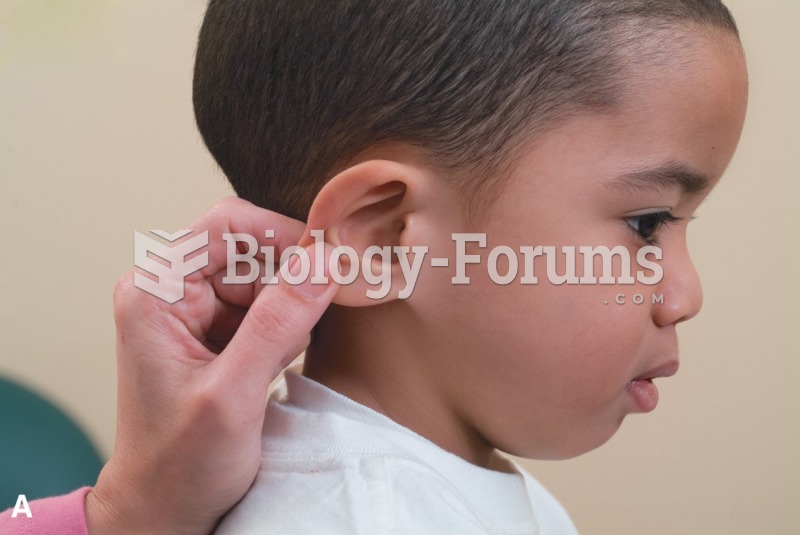
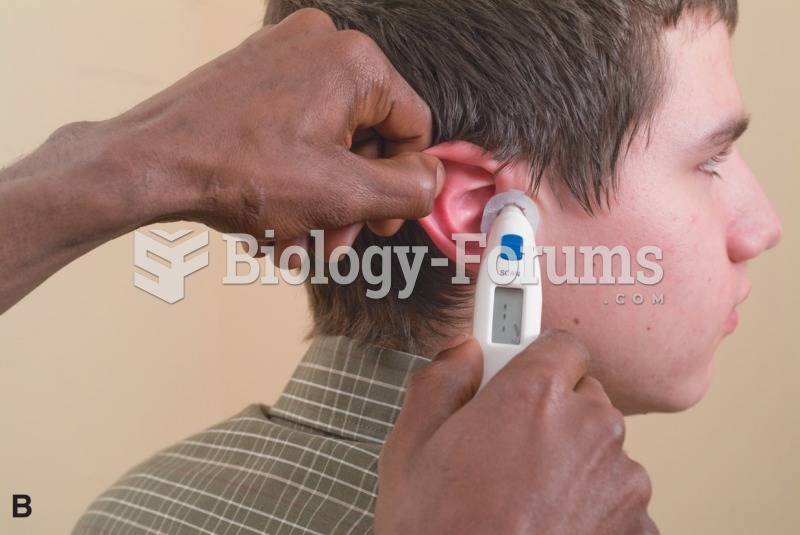
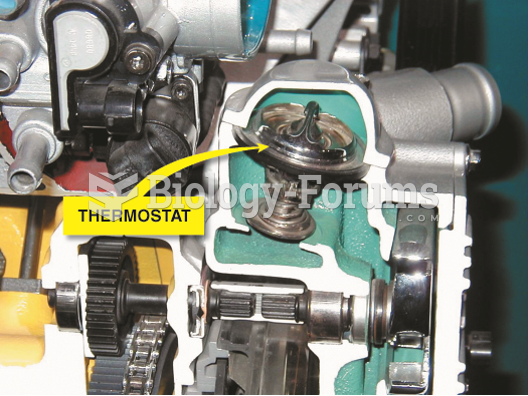
An object transfers heat when its temperature is raised by contact with a
Question 2A material through which heat conducts slowly is called a __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 3A piston compresses a gas, while at the same time heat is lost to the surroundings. The temperature of the gas rises. This is governed by the __________ law of thermodynamics.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 4The air temperature where the humidity reaches the saturation density is called the ___________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 5In a steam engine, steam at 140C in a turbine does work on an external system, and the steam leaves the turbine at 100C. The efficiency of the steam engine is 5. The relevant physical principle is the __________ law of thermodynamics.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 6At 96F the saturation density of air is 0.04 kg/m3 . If the weather report says the relative humidity is 90 when the temperature is 96F, the humidity is __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 7The Eiffel tower in Paris is made primarily of iron, whose coefficient of linear expansion is about 10 106/C. On a cold day when the temperature is 10C the Eiffel tower is 300 meters tall. Its height on a hot day when the temperature is 40C is __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 8specific heat capacity of ice = 2,000 J/kg-C latent heat of fusion of water = 334,000 J/kg specific heat capacity of water = 4,000 J/kg-C After the 1 kg block of ice melts, the amount of heat required to raise its temperature to 10C is __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 9specific heat capacity of ice = 2,000 J/kg-C latent heat of fusion of water = 334,000 J/kg specific heat capacity of water = 4,000 J/kg-C As the ice is melting, the temperature of the ice-water mixture rises by __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 10specific heat capacity of ice = 2,000 J/kg-C latent heat of fusion of water = 334,000 J/kg specific heat capacity of water = 4,000 J/kg-C The 1 kg block of ice melts into water. The amount of heat absorbed by the ice as it melts is __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 11Specific heat capacity of ice = 2,000 J/kg-C latent heat of fusion of water = 334,000 J/kg specific heat capacity of water = 4,000 J/kg-C A 1 kg block of ice is removed from a freezer where its temperature was 10C. The amount of heat absorbed by the ice as it warms to 0C is __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 12Natural processes tend to increase the __________ of thermodynamic systems.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 13Two ways that the temperature of a gas can be increased are by __________ and __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 14The latent heat of vaporization of water is roughly 10 times the latent heat of fusion of water. The amount of heat required to boil 1 kg of water is __________ times the amount of heat required to melt 1 kg of ice.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 15The specific heat capacity of water is about twice the specific heat capacity of ice. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water 10C is __________ times the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of ice 10C.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 16When water boils, its temperature __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 17When ice melts, its temperature __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 18The specific heat capacity of copper is three times the specific heat capacity of lead. Equal masses of copper and lead are heated from room temperature to the temperature of boiling water. To achieve this, the amount of heat added to the copper is __________ times the amount of heat added to the lead.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 19The coefficient of linear expansion of ordinary glass is three times that of Pyrex glass. An ordinary glass rod and a Pyrex glass rod of equal lengths at room temperature are dropped into boiling water. The change in length of the ordinary glass rod will be __________ times the change in length of the Pyrex glass rod.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 20__________ is transferred from a substance if it is exposed to something that has a lower temperature.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 21Two ways that the internal energy of a substance can be increased are __________ and __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 22Three examples of a heat mover are __________, __________, and __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 23A bimetallic strip is usable as a thermometer because of the property of __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 24Heating the air in a hot air balloon reduces the air's _________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 25A hot pizza contains __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 26As the air cools at night the relative humidity usually __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 27A wood stove in the corner of a cabin causes the entire cabin to become heated. This is an example of __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 28The warmth you feel from the Sun at the beach is an example of __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 29You hold one end of a solid rod in a fire, and the other end becomes hot. This is an example of __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 30The temperature scale where the numerical value is proportional to the average kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules is __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 31The lowest temperature is called ______________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 32A bimetallic strip is formed from two materials that have different __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 33Two devices that make use of a bimetallic strip are a __________ and a __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 34The first law of thermodynamics is basically a special version of the law of ______________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 35The average kinetic energy of the atoms in a spoon determines its __________.
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Question 36Internal energy in a system can be changed by
a. doing work on the system. b. increasing the specific heat in the system.
c. changing the temperature of the system. d. transferring heat to/from the system.
Question 37The internal energy of a substance can be increased by
a. doing work on it.
b. letting it do work.
c. adding heat to it.
d. extracting heat from it.
e. none of the above.
Question 38The internal energy of air can be increased by
a. compressing it. b. allowing heat to flow into it.
c. lifting it. d. allowing it to expand.
Question 39Solar energy
a. is a recent invention.
b. has been used for a long time.
c. has not yet been successfully developed.
d. is indirectly the source of most of the energy we use.
Question 40Stepping barefoot off a rug onto a hardwood floor makes your feet feel cold. Why?
a. The hardwood floor is at a lower temperature than the rug.
b. The hardwood floor is at a lower temperature than your feet.
c. The hardwood floor conducts heat away from your feet better than the rug.
d. all of the above
Question 41Absolute zero is
a. 0 K. b. 459.67F.
c. 273.15C. d. 0 on any temperature scale.
Question 42In the first law of thermodynamics, the work can be
a. only positive. b. only negative.
c. neither. d. either positive or negative.
Question 43The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of energy required to raise 1 kg of the substance by a temperature of
a. 1F. b. 10 C.
c. 10 F. d. 1C.
Question 44As long as there is ice in your drink, the temperature of the ice remains near
a. room temperature. b. the temperature of the drink.
c. zero Celsius. d. zero Fahrenheit.
Question 45Heat flows from
a. cold to hot. b. hot to cold.
c. Kelvin to Celsius. d. the same as temperature.
Question 46Heat transfer by radiation occurs via
a. electromagnetic waves.
b. nuclear decay.
c. molecular collisions.
d. the solar wind.
e. none of the above.
Question 47A piston compresses a gas, while at the same time heat is lost to the surroundings. The temperature of the gas rises. The amount of temperature rise is governed by
a. the first law of thermodynamics.
b. the second law of thermodynamics.
c. specific heat capacity.
d. a heat pump.
e. none of the above.
Question 48The efficiency of a heat engine
a. can never exceed the Carnot efficiency.
b. can be improved by lowering the temperature of the cool reservoir.
c. can be improved by raising the temperature of the hot reservoir.
d. all of the above
Question 49In a steam engine, steam at 140C in a turbine does work on an external system, and the steam leaves the turbine at 100C. The efficiency of the steam engine is 5. The relevant physical principle is
a. the first law of thermodynamics.
b. the second law of thermodynamics.
c. specific heat capacity.
d. operation of a heat pump.
e. none of the above.
Question 50Even when the temperature of a pan of water is below the boiling point, some water still evaporates. This is because
a. of convection.
b. the kinetic energies of individual water molecules vary above and below the average value.
c. the humidity always increases.
d. none of the above
Question 51Air at a temperature of 32 F has a relative humidity of 60. If the temperature of the same air rises to 40 F, the relative humidity
a. stays the same.
b. increases.
c. decreases.
d. cannot be determined.
Question 52At 96 F the saturation density of air is 0.04 kg/m3 . If the weather report says the relative humidity is 90 when the temperature is 96F, the humidity is
a. 10 .
b. 0.9.
c. 0.004 kg/m3.
d. 0.036 kg/m3.
e. 0.04 kg/m3.
Question 53Why do bridges have expansion joints?
a. They would buckle and crack otherwise.
b. to let water run off
c. to absorb vibrations due to traffic
d. for ease in construction
Question 54The Eiffel tower in Paris is made primarily of iron, whose coefficient of linear expansion is about 10 106/C. On a cold day when the temperature is 10C the Eiffel tower is 300 meters tall. Its height on a hot day when the temperature is 40C is
a. 300.0015 m.
b. 300.015 m.
c. 300.15 m.
d. 301.5 m.
e. 315 m.
Question 55specific heat capacity of ice = 2,000 J/kg-C latent heat of fusion of water = 334,000 J/kg specific heat capacity of water = 4,000 J/kg-C After the 1 kg block of ice melts, the amount of heat required to raise its temperature to 10 C is
a. 2,000 J.
b. 4,000 J.
c. 20,000 J.
d. 40,000 J.
e. 334,000 J.
Question 56specific heat capacity of ice = 2,000 J/kg-C latent heat of fusion of water = 334,000 J/kg specific heat capacity of water = 4,000 J/kg-C As the ice is melting, the temperature of the ice-water mixture rises by
a. 0C.
b. +5C.
c. 5C.
d. +10C.
e. 10C.
Question 57specific heat capacity of ice = 2,000 J/kg-C latent heat of fusion of water = 334,000 J/kg specific heat capacity of water = 4,000 J/kg-C The 1 kg block of ice melts into water. The amount of heat absorbed by the ice as it melts is
a. 2,000 J.
b. 4,000 J.
c. 20,000 J.
d. 40,000 J.
e. 334,000 J.
Question 58specific heat capacity of ice = 2,000 J/kg-C latent heat of fusion of water = 334,000 J/kg specific heat capacity of water = 4,000 J/kg-C A 1 kg block of ice is removed from a freezer where its temperature was 10C. The amount of heat absorbed by the ice as it warms to 0C is
a. 2,000 J.
b. 4,000 J.
c. 20,000 J.
d. 40,000 J.
e. 334,000 J.
Question 59Which mechanism(s) of heat transfer will work in a vacuum?
a. conduction b. convection
c. radiation d. none of the above
Question 60The temperature of a gas can be increased by
a. compressing it.
b. adding heat to it.
c. doing work on it.
d. all of the above.
e. none of the above.
Question 61The latent heat of vaporization of water is roughly 10 times the latent heat of fusion of water. The amount of heat required to boil away 1 kg of water is __________ the amount of heat required to melt 1 kg of ice.
a. one tenth
b. equal to
c. 10 times
d. unrelated to
Question 62The specific heat capacity of water is about twice the specific heat capacity of ice. From this information, the amount of heat required to boil 1 kg of water is ________ the amount of heat required to melt 1 kg of ice.
a. 1/2 b. equal to
c. 2 times d. unrelated to
Question 63What's wrong with the statement heat rises?
a. Nothingheat does rise.
b. One should say energy rises..
c. One should say heated air (or other fluid) rises..
d. none of the above
Question 64Natural processes tend to increase the __________ of thermodynamic systems.
a. temperature b. internal energy
c. Carnot efficiency d. entropy
Question 65When droplets of condensation form on the outside of a glass of ice water, it must be that in the air right next to the glass
a. the temperature is near the dew point.
b. the humidity is near the saturation density.
c. the relative humidity is near 100.
d. all of the above
Question 66When water boils, its temperature
a. increases. b. decreases.
c. stays constant. d. cannot be determined.
Question 67When ice melts, its temperature
a. increases. b. decreases.
c. stays constant. d. cannot be determined.
Question 68The specific heat capacity of copper is three times the specific heat capacity of lead. Equal masses of copper and lead are heated from room temperature to the temperature of boiling water. To achieve this, the amount of heat added to the copper is ___________ the amount of heat added to the lead.
a. 1/9
b. 1/3
c. equal to
d. 3 times
e. 9 times
Question 69The coefficient of linear expansion of ordinary glass is three times that of Pyrex glass. An ordinary glass rod and a Pyrex glass rod of equal lengths at room temperature are dropped into boiling water. The change in length of the ordinary glass rod will be ___________ the change in length of the Pyrex glass rod.
a. 1/9
b. 1/3
c. equal to
d. 3 times
e. 9 times
Question 70The change in size of an object due to thermal expansion depends upon
a. what the object is made of.
b. the object's original size.
c. how much the temperature changes.
d. A and C.
e. all of the above.
Question 71The total kinetic and potential energies of all the atoms and molecules of a substance is its
a. heat.
b. internal energy.
c. temperature.
d. thermodynamics.
e. none of the above
Question 72A hot pizza contains
a. heat.
b. internal energy.
c. temperature.
d. work.
e. none of the above.
Question 73The amount of heat energy a refrigerator removes from the food stored inside it is ___________ the amount of electrical energy required to run the refrigerator.
a. equal to b. greater than
c. less than d. unrelated to
Question 74An example of a heat mover is
a. a refrigerator.
b. an air conditioner.
c. a heat pump.
d. all of the above.
e. none of the above.
Question 75A bimetallic strip is usable as a thermometer because of
a. heat conduction.
b. heat convection.
c. heat radiation.
d. thermal expansion.
e. none of the above.
Question 76Firewalkers step on the hot ashes and coals from a wood fire without getting their feet burned. How might this be possible?
a. They have magical powers.
b. The ashes are poor conductors of heat.
c. They do get burned but enjoy the publicity.
d. none of the above
Question 77The lunar surface cools after the Sun sets. This is an example of
a. heat conduction.
b. heat convection.
c. heat radiation.
d. thermal expansion.
e. none of the above.
Question 78A piece of chocolate melts in your mouth. This is an example of
a. heat conduction.
b. heat convection.
c. heat radiation.
d. thermal expansion.
e. none of the above.
Question 79A wood stove in the corner of a cabin causes the entire cabin to become heated. This is an example of
a. heat conduction.
b. heat convection.
c. heat radiation.
d. thermal expansion.
e. none of the above.
Question 80The warmth you feel from the Sun at the beach is an example of
a. heat conduction.
b. heat convection.
c. heat radiation.
d. thermal expansion.
e. none of the above.
Question 81You hold one end of a solid rod in a fire, and the other end becomes hot. This is an example of
a. heat conduction.
b. heat convection.
c. heat radiation.
d. thermal expansion.
e. none of the above.
Question 82In a gas of different types of molecules all at the same temperature, the speeds of the heavier molecules will generally be _____________ the speeds of the lighter molecules.
a. the same as b. greater than
c. less than d. unrelated to
Question 83Temperature measures
a. how much heat is in a substance.
b. the internal energy of an object.
c. the average speed of atoms and molecules in a substance.
d. the average kinetic energy of atoms and molecules in a substance.
Question 84Which of these is stated properly?
a. The temperature of liquid nitrogen is 77 Kelvin..
b. The temperature of liquid nitrogen is 77 Kelvins..
c. The temperature of liquid nitrogen is 77 degrees Kelvin..
d. The temperature of liquid nitrogen is 77 Kelvin degrees..
Question 85Which are biggerCelsius degrees or Fahrenheit degrees?
a. Fahrenheit
b. Celsius
c. Neitherthey are the same size.
d. This is a nonsensical comparison.
Question 86The temperature scale where the numerical value is proportional to the average kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules is
a. Fahrenheit. b. Celsius.
c. Kelvin. d. none of the above.
Question 87A key is placed in a hot oven and warmed to 100C. As a result
a. the hole in the key becomes smaller.
b. the key is bent into an arc.
c. the key becomes longer.
d. all of the above.
Question 88A bimetallic strip is formed from two materials that have different
a. coefficients of linear expansion.
b. heat capacities.
c. calories.
d. phase transitions.
e. relative humidities.
Question 89A device that makes use of a bimetallic strip is
a. a thermometer.
b. a thermostat.
c. a choke control in an old automobile.
d. all of the above.
e. none of the above.
Question 90One food calorie equals
a. 1 calorie. b. 100 calories.
c. 1000 calories. d. none of the above.
Question 91Which is larger, a calorie or a joule?
a. calorie
b. joule
c. Neitherthey are the same.
d. They cannot be compared since they measure different physical quantities.
Question 92When a substance is exposed to something that has a lower temperature,
a. work is done on it.
b. work is done by it.
c. heat is transferred from it.
d. heat is transferred to it.
e. none of the above.
Question 93Internal energy can only be changed by adding heat
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 94The dew point is the temperature at which a given humidity equals the saturation density.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 95Evaporation is when a gas is converted into a liquid.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 96Temperature is a measure of heat.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 97A piston compresses a gas, while at the same time heat is lost to the surroundings. The temperature of the gas rises. This is governed by the second law of thermodynamics.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 98In a steam engine, steam at 140C in a turbine does work on an external system, and the steam leaves the turbine at 100C. The efficiency of the steam engine is 5. The relevant physical principle is the first law of thermodynamics.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 99Air at a temperature of 32F has a relative humidity of 60. If the temperature of the same air increases, the relative humidity increases.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 100At 96F the saturation density of air is 0.04 kg/m3 . If the weather report says the relative humidity is 90 when the temperature is 96F, the humidity is 0.036 kg/m3.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 101The Eiffel tower in Paris is made primarily of iron, whose coefficient of linear expansion is about 10 106/C. On a cold day when the temperature is 10C the Eiffel tower is 300 meters tall. Its height on a hot day when the temperature is 40C is 300.15 m.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 102specific heat capacity of ice = 2,000 J/kg-C latent heat of fusion of water = 334,000 J/kg specific heat capacity of water = 4,000 J/kg-C After the 1 kg block of ice melts, the amount of heat required to raise its temperature to 10C is 3,340,000 J.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 103specific heat capacity of ice = 2,000 J/kg-C latent heat of fusion of water = 334,000 J/kg specific heat capacity of water = 4,000 J/kg-C As the ice is melting, the temperature of the ice-water mixture rises by 10C.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 104specific heat capacity of ice = 2,000 J/kg-C latent heat of fusion of water = 334,000 J/kg specific heat capacity of water = 4,000 J/kg-C The 1 kg block of ice melts into water. The amount of heat absorbed by the ice as it melts is 334,000 J.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 105specific heat capacity of ice = 2,000 J/kg-C latent heat of fusion of water = 334,000 J/kg specific heat capacity of water = 4,000 J/kg-C A 1 kg block of ice is removed from a freezer where its temperature was 10C. The amount of heat absorbed by the ice as it warms to 0C is 20,000 J.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 106A liquid cannot be heated simultaneously by conduction, convection, and radiation.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 107You can increase the temperature of a gas by compressing it.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 108The latent heat of vaporization of water is roughly 10 times the latent heat of fusion of water. The amount of heat required to boil away 1 kg of water is 10 times the amount of heat required to melt 1 kg of ice.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 109The specific heat capacity of water is about twice the specific heat capacity of ice. The amount of heat required to boil 1 kg of water is twice the amount of heat required to melt 1 kg of ice.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 110Water is good for putting out fires because it has a very high latent heat of vaporization.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 111When water boils, its temperature increases.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 112When you add heat to ice, its temperature always stays constant.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 113When ice melts, its temperature increases.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 114The specific heat capacity of copper is three times the specific heat capacity of lead. Equal masses of copper and lead are heated from room temperature to the temperature of boiling water. To achieve this, the amount of heat added to the copper is 3 times the amount of heat added to the lead.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 115The coefficient of linear expansion of ordinary glass is three times that of Pyrex glass. An ordinary glass rod and a Pyrex glass rod of equal lengths at room temperature are dropped into boiling water. The change in length of the ordinary glass rod will be 3 times the change in length of the Pyrex glass rod.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 116Natural processes tend to increase the entropy of thermodynamic systems.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 117You can increase the internal energy of a gas by heating it or by compressing it.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 118A steam turbine is an example of a heat mover.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 119As the air cools at night the relative humidity usually drops.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 120A refrigerator is an example of a heat mover.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 121A bimetallic strip is usable in a thermometer because of its heat capacity.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 122A wood stove in the corner of a cabin causes the entire cabin to become heated because of heat conduction.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 123You feel warm from the Sun at the beach because of heat radiation.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 124When you hold one end of a solid rod in a fire, the other end becomes hot because of heat convection.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 125On the Kelvin scale the temperature is proportional to the average kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules whose temperature is being measured.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 126A hot pizza contains heat.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 127Celsius degrees are larger than Fahrenheit degrees.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 128A bimetallic strip is formed from two materials that have different heat capacities.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 129A thermostat can work because of a bimetallic strip.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 130One food calorie equals 1000 calories.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 131A barometer can work because of a bimetallic strip.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 132Heat is transferred from a substance if it is exposed to something that has a lower temperature.
a. True
b. False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Question 133The cabin pressure of a passenger jet cruising at high altitude (30,000 ft) is about 1 atm. and the pressure outside is about 0.3 atm. What is the outward force acting on a door measuring 1 meter by 2 meters? (Hint: convert metric to English units in this problem using the conversion factor m2 to ft2 in the Table of Conversion Factors)