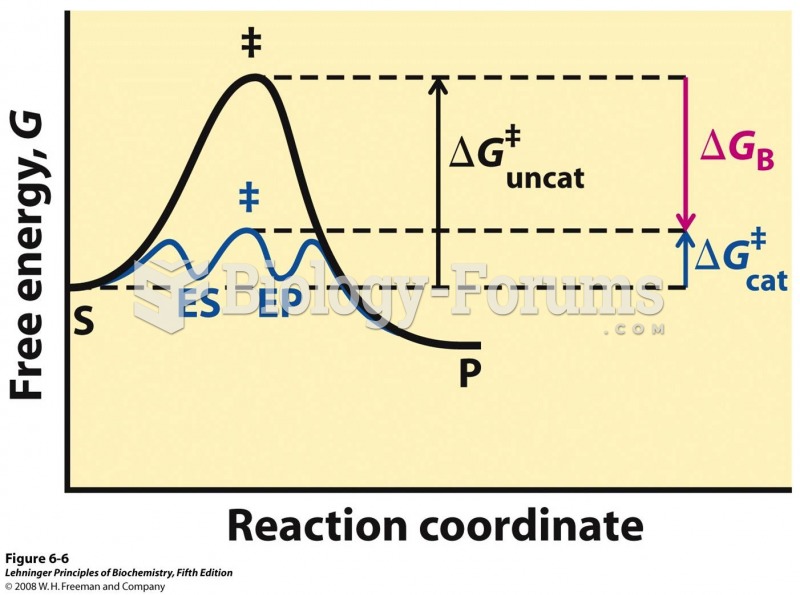
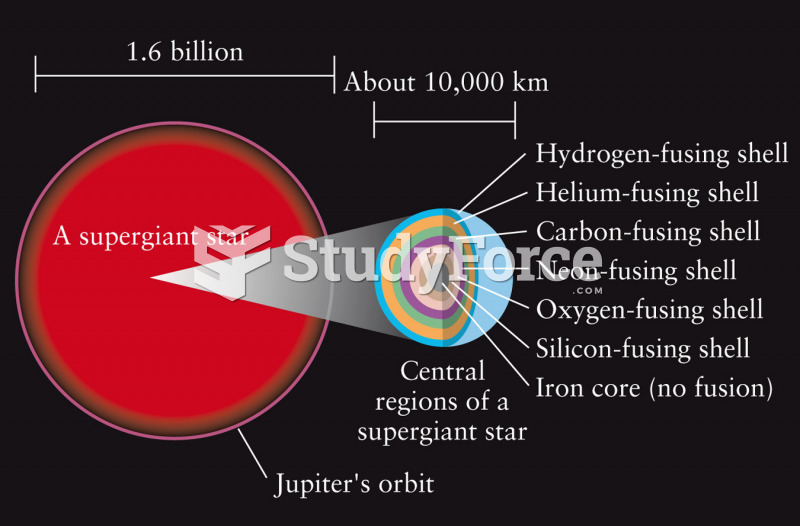
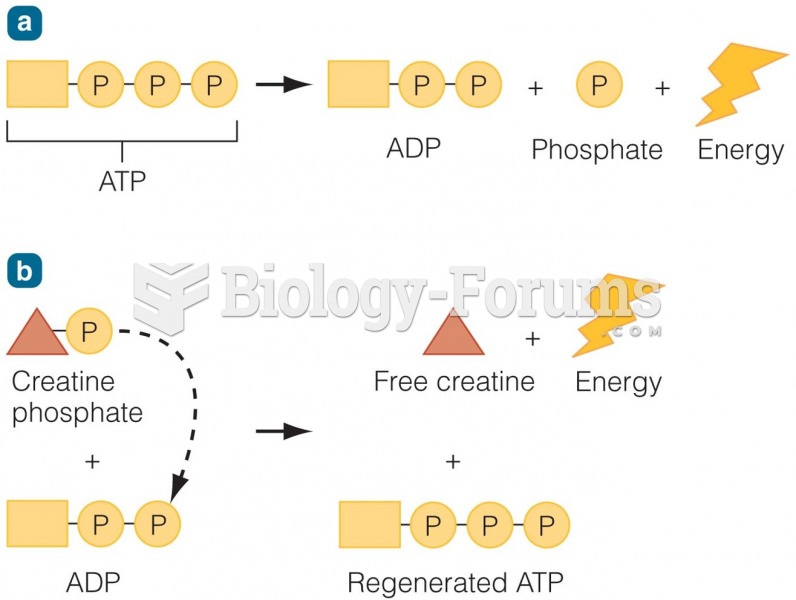
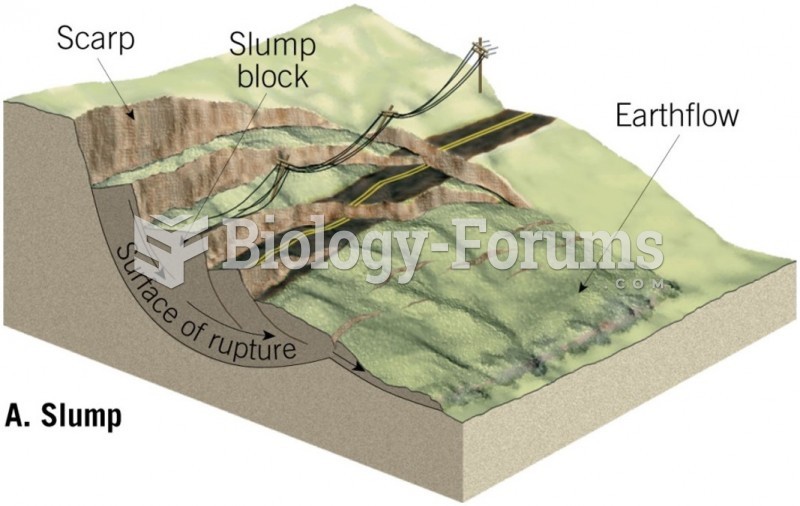
|
|
|
About one in five American adults and teenagers have had a genital herpes infection—and most of them don't know it. People with genital herpes have at least twice the risk of becoming infected with HIV if exposed to it than those people who do not have genital herpes.
Sperm cells are so tiny that 400 to 500 million (400,000,000–500,000,000) of them fit onto 1 tsp.
In the United States, congenital cytomegalovirus causes one child to become disabled almost every hour. CMV is the leading preventable viral cause of development disability in newborns. These disabilities include hearing or vision loss, and cerebral palsy.
Most strokes are caused when blood clots move to a blood vessel in the brain and block blood flow to that area. Thrombolytic therapy can be used to dissolve the clot quickly. If given within 3 hours of the first stroke symptoms, this therapy can help limit stroke damage and disability.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.