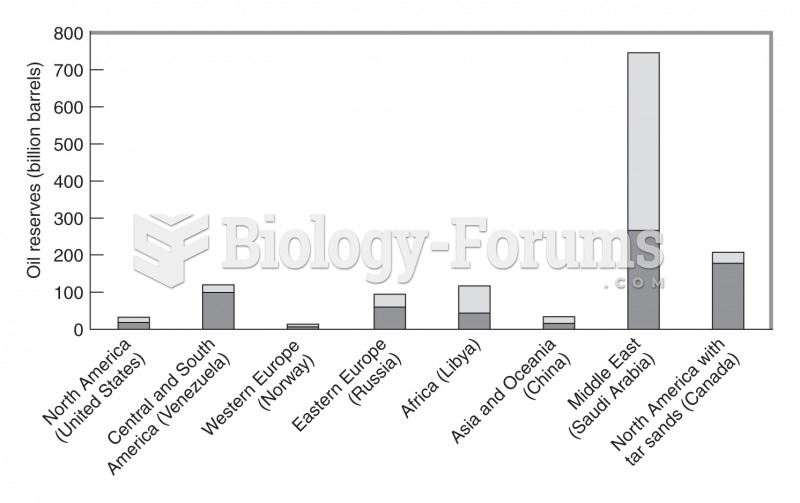
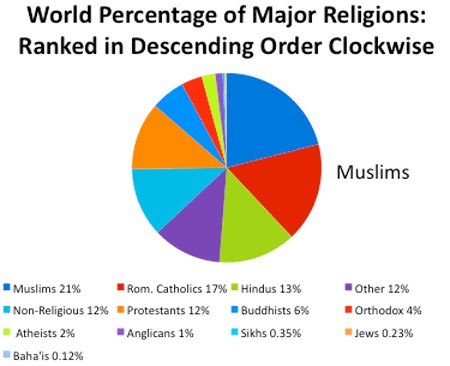
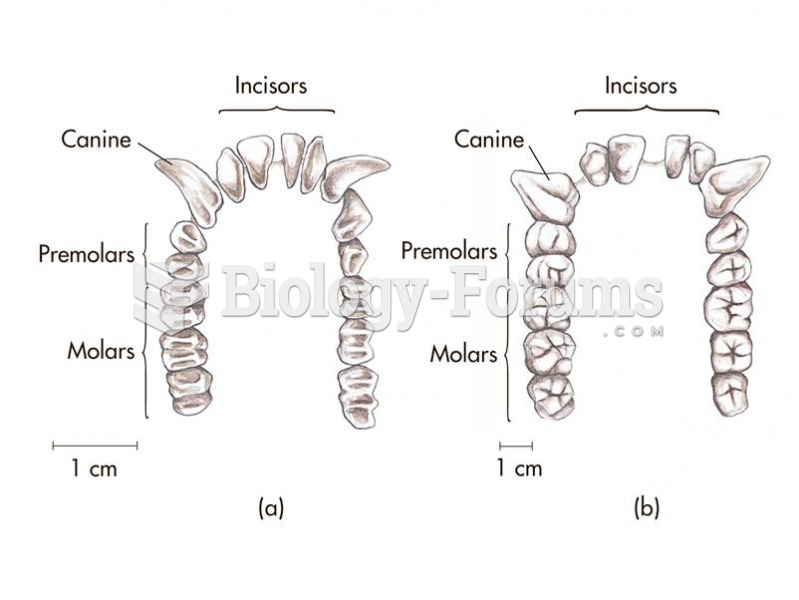
|
|
|
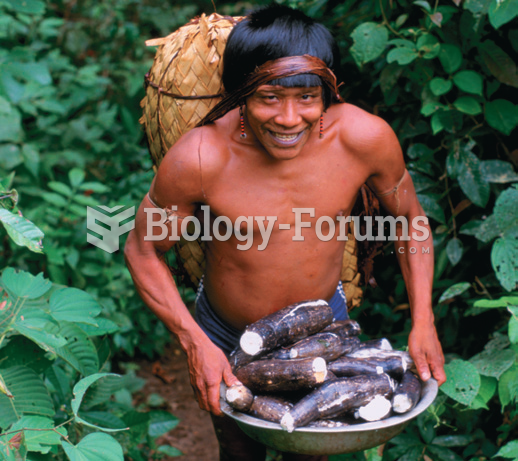
Tobacco depletes the body of vitamins A, C, and E, which can result in any of the following: dry hair, dry skin, dry eyes, poor growth, night blindness, abscesses, insomnia, fatigue, reproductive system problems, sinusitis, pneumonia, frequent respiratory problems, skin disorders, weight loss, rickets, osteomalacia, nervousness, muscle spasms, leg cramps, extremity numbness, bone malformations, decayed teeth, difficulty in walking, irritability, restlessness, profuse sweating, increased uric acid (gout), joint damage, damaged red blood cells, destruction of nerves, infertility, miscarriage, and many types of cancer.
The term pharmacology is derived from the Greek words pharmakon("claim, medicine, poison, or remedy") and logos ("study").
People with alcoholism are at a much greater risk of malnutrition than are other people and usually exhibit low levels of most vitamins (especially folic acid). This is because alcohol often takes the place of 50% of their daily intake of calories, with little nutritional value contained in it.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA was discovered in 1961 in the United Kingdom. It if often referred to as a superbug. MRSA infections cause more deaths in the United States every year than AIDS.
About 3.2 billion people, nearly half the world population, are at risk for malaria. In 2015, there are about 214 million malaria cases and an estimated 438,000 malaria deaths.