|
|
|
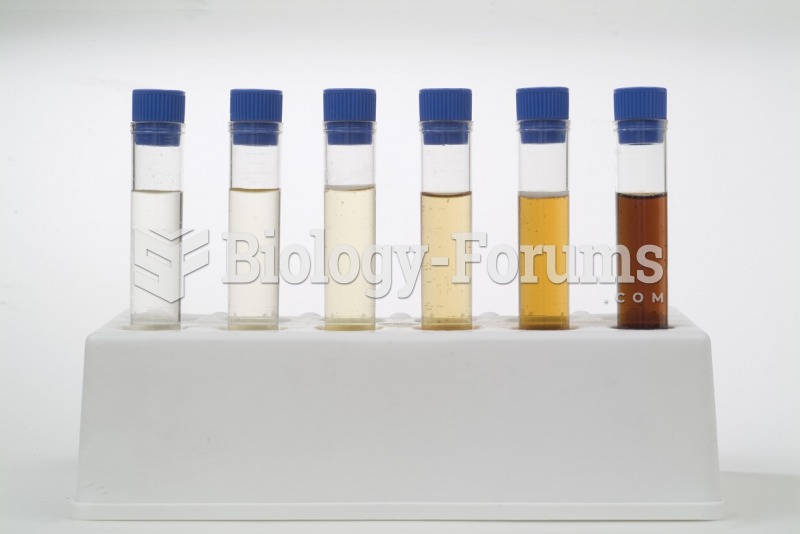
The calories found in one piece of cherry cheesecake could light a 60-watt light bulb for 1.5 hours.
Prostaglandins were first isolated from human semen in Sweden in the 1930s. They were so named because the researcher thought that they came from the prostate gland. In fact, prostaglandins exist and are synthesized in almost every cell of the body.
Asthma-like symptoms were first recorded about 3,500 years ago in Egypt. The first manuscript specifically written about asthma was in the year 1190, describing a condition characterized by sudden breathlessness. The treatments listed in this manuscript include chicken soup, herbs, and sexual abstinence.
Bacteria have been found alive in a lake buried one half mile under ice in Antarctica.
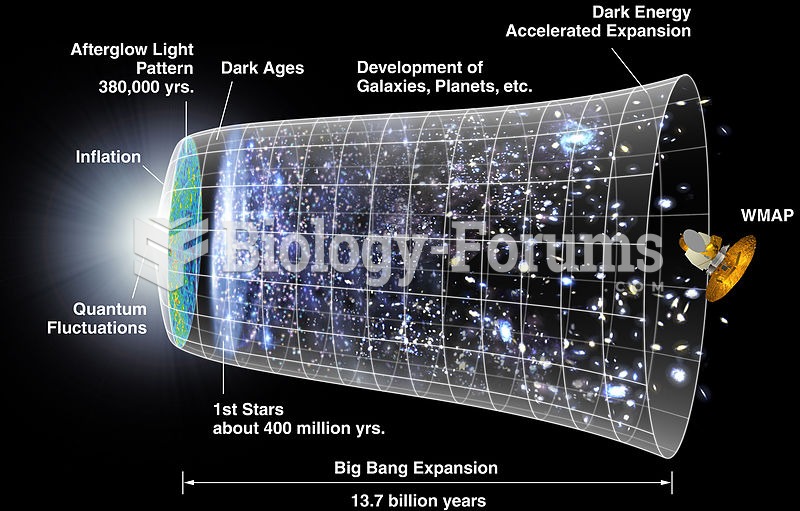
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.