This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Signs and symptoms of a drug overdose include losing consciousness, fever or sweating, breathing problems, abnormal pulse, and changes in skin color.
Did you know?
Serum cholesterol testing in adults is recommended every 1 to 5 years. People with diabetes and a family history of high cholesterol should be tested even more frequently.
Did you know?
About 100 new prescription or over-the-counter drugs come into the U.S. market every year.
Did you know?
The top five reasons that children stay home from school are as follows: colds, stomach flu (gastroenteritis), ear infection (otitis media), pink eye (conjunctivitis), and sore throat.
Did you know?
A seasonal flu vaccine is the best way to reduce the chances you will get seasonal influenza and spread it to others.
 EEG recordings showing the differences between normal, absence seizure, and generalized tonic–clonic
EEG recordings showing the differences between normal, absence seizure, and generalized tonic–clonic
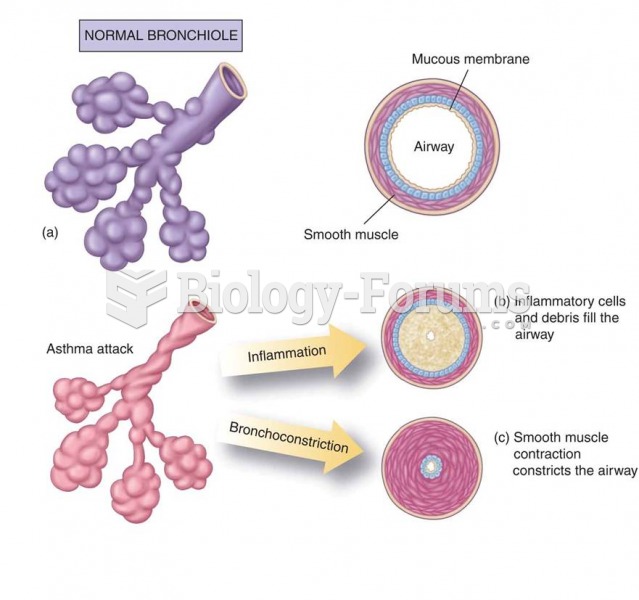 Changes in the bronchioles during an asthma attack: (a) Normal bronchiole; (b) the inflammatory comp
Changes in the bronchioles during an asthma attack: (a) Normal bronchiole; (b) the inflammatory comp