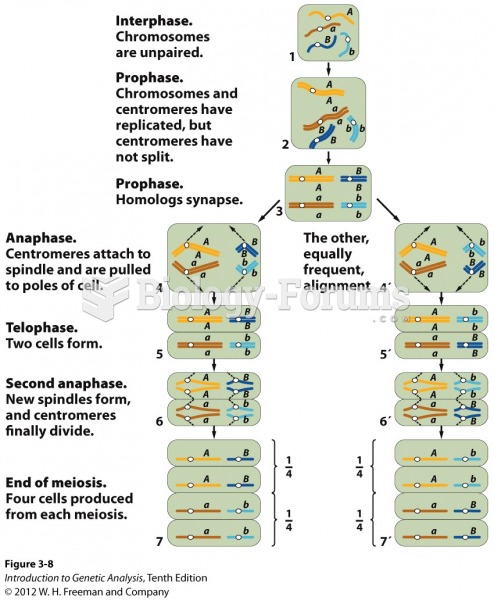
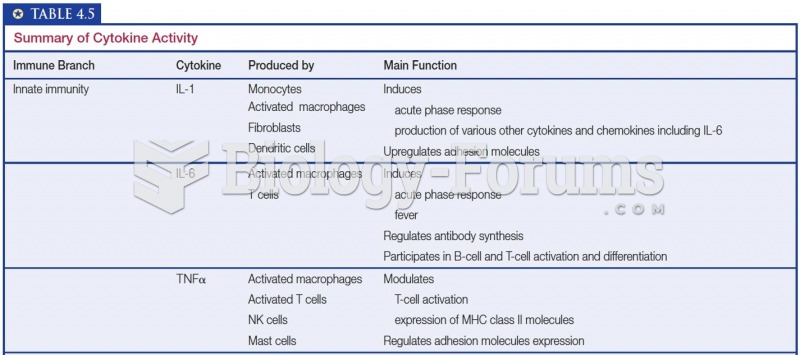
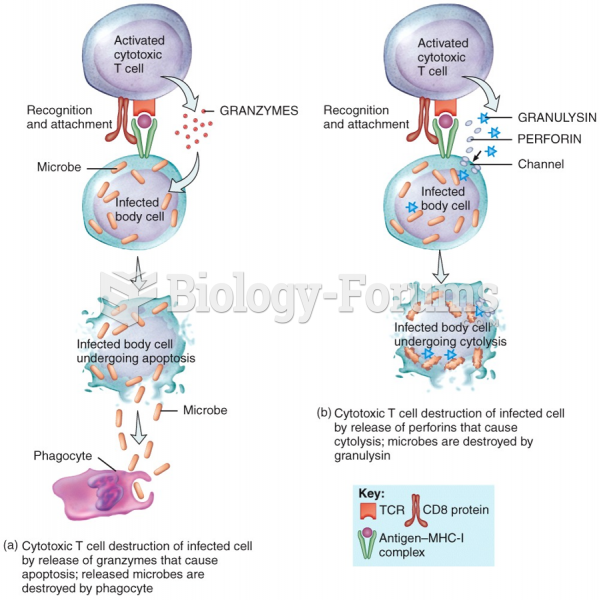
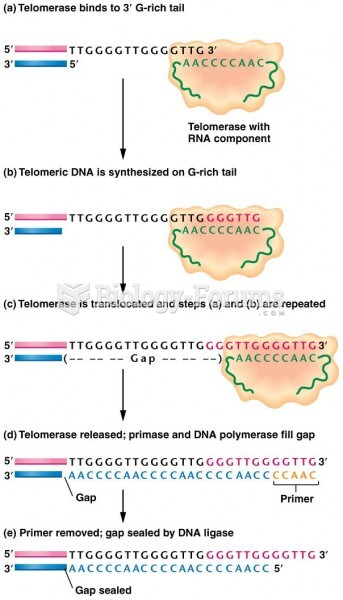
- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
|
|
|
- Grade 11 and 12 Mathematics (Moderator: geoffrey)
The word drug comes from the Dutch word droog (meaning "dry"). For centuries, most drugs came from dried plants, hence the name.
Patients should never assume they are being given the appropriate drugs. They should make sure they know which drugs are being prescribed, and always double-check that the drugs received match the prescription.
Eating carrots will improve your eyesight. Carrots are high in vitamin A (retinol), which is essential for good vision. It can also be found in milk, cheese, egg yolks, and liver.
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
There used to be a metric calendar, as well as metric clocks. The metric calendar, or "French Republican Calendar" divided the year into 12 months, but each month was divided into three 10-day weeks. Each day had 10 decimal hours. Each hour had 100 decimal minutes. Due to lack of popularity, the metric clocks and calendars were ended in 1795, three years after they had been first marketed.