|
|
|
Cocaine was isolated in 1860 and first used as a local anesthetic in 1884. Its first clinical use was by Sigmund Freud to wean a patient from morphine addiction. The fictional character Sherlock Holmes was supposed to be addicted to cocaine by injection.
HIV testing reach is still limited. An estimated 40% of people with HIV (more than 14 million) remain undiagnosed and do not know their infection status.
People with high total cholesterol have about two times the risk for heart disease as people with ideal levels.
About 60% of newborn infants in the United States are jaundiced; that is, they look yellow. Kernicterus is a form of brain damage caused by excessive jaundice. When babies begin to be affected by excessive jaundice and begin to have brain damage, they become excessively lethargic.
The first war in which wide-scale use of anesthetics occurred was the Civil War, and 80% of all wounds were in the extremities.
 An offset screwdriver is used to install or remove fasteners that do not have enough space above to ...
An offset screwdriver is used to install or remove fasteners that do not have enough space above to ...
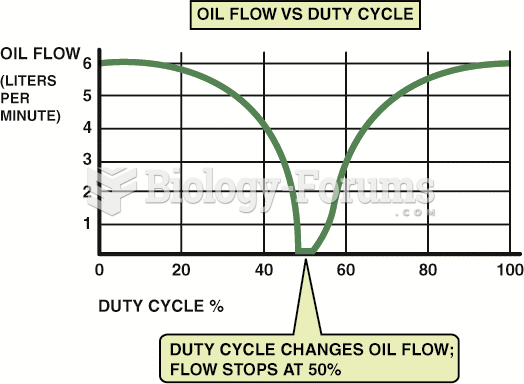
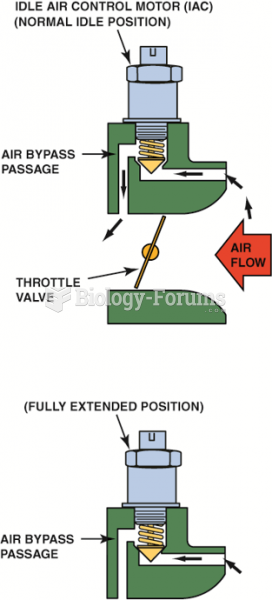
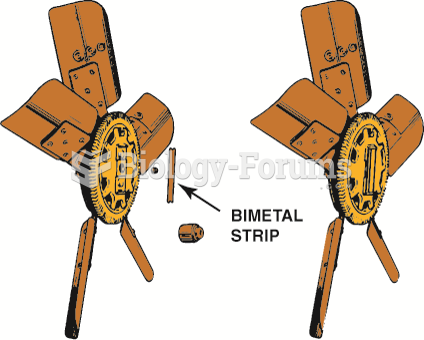 The bimetallic temperature sensor spring controls the amount of silicone that is allowed into the ...
The bimetallic temperature sensor spring controls the amount of silicone that is allowed into the ...