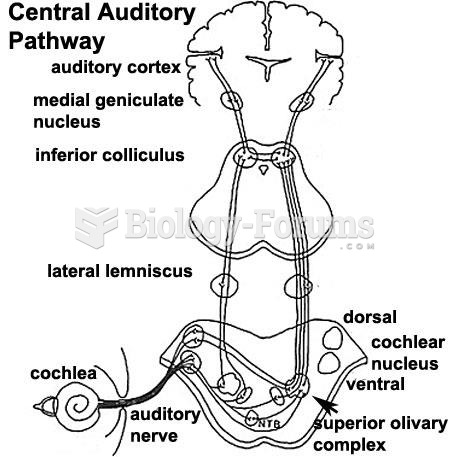
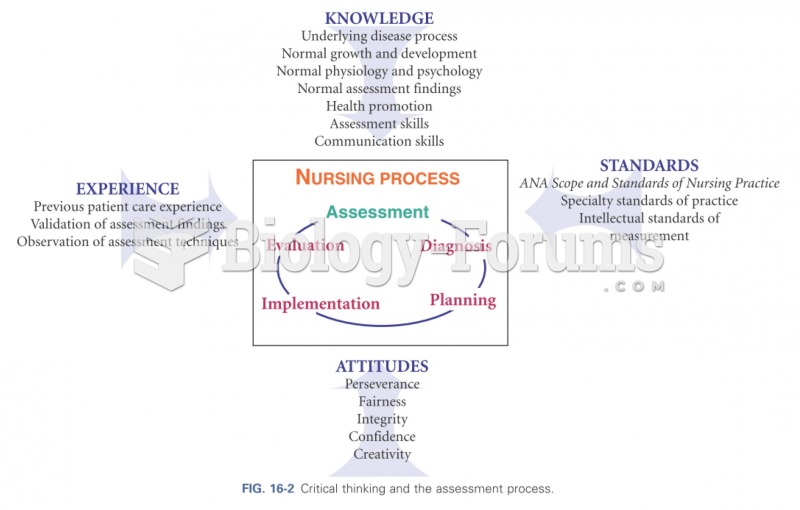
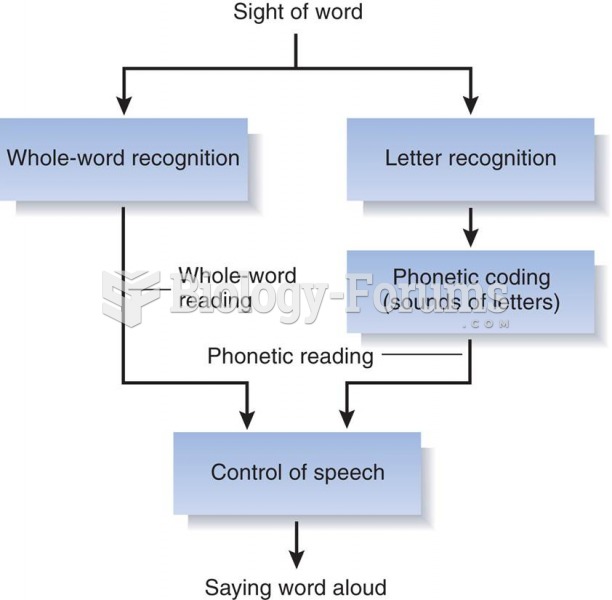
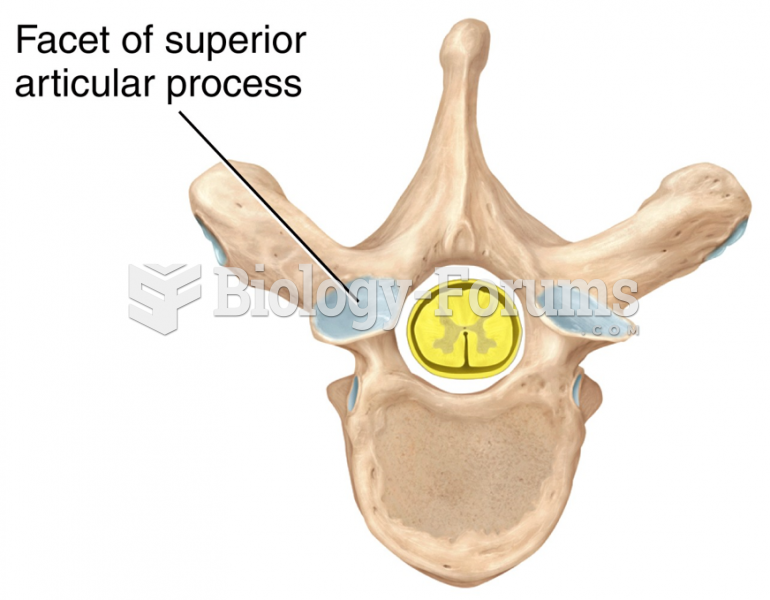
Answer to Question 1
The primary purpose of federal bankruptcy law is to discharge the debtor from burdensome debts, known as a fresh start.. Chapter 7 liquidation bankruptcy (also called straight bankruptcy) is the most familiar form of bankruptcy. In this type of proceeding, the debtor's nonexempt property is sold for cash, the cash is distributed to the creditors, and any unpaid debts are discharged. Any person, including individuals, partnerships, and corporations, may be a debtor in a Chapter 7 proceeding. A Chapter 7 bankruptcy is commenced when a petition is filed with the bankruptcy court. The petition may be filed by either the debtor (voluntary) or one or more creditors (involuntary). Voluntary petitions only have to state that the debtor has debts; insolvency need not be declared. The petition must be signed and sworn to under oath. Married couples may file a joint petition. An involuntary petition must allege that the debtor is not paying his or her debts as they become due. The filing of the petition automatically staysto wit, suspendscertain action by creditors against the debtor or the debtor's property. This is called an automatic stay. The stay, which applies to secured and unsecured creditors, is designed to prevent a scramble of the debtor's assets in a variety of court proceedings. The bankruptcy estate includes all the debtor's legal and equitable interests in all types of property, wherever located, existing when the petition is filed. Because the Bankruptcy Code is not designed to make the debtor a pauper, certain property is exempt from the bankruptcy estate. The debtor may retain exempt property, either through the operation of the federal exemption or state exemption scheme. Under Chapter 7, the nonexempt property of the bankruptcy estate must be distributed to the debtor's secured and unsecured creditors. Secured creditors have priority over unsecured creditors. If the value of the collateral exceeds the secured interest, the excess becomes available to satisfy the claims of the debtor's unsecured creditors. After the property is distributed to satisfy the allowed claims, the remaining unpaid claims are discharged, which means the debtor is no longer legally responsible for them. Only individuals may be granted a discharge. Discharge is not available to partnerships and corporations. These entities must liquidate under state law before or upon completion of the Chapter 7 proceedings. A debtor can be granted a discharge in a Chapter 7 proceeding only once every six years.
Answer to Question 2
True