Answer to Question 1
A legal intersection occurs when one area of legal practice is influenced by another. Bankruptcy is a specialty that is not confined to just one field of practice. Attorneys and paralegals are well aware that although bankruptcy is considered a specialized field of practice, an understanding of how other areas of law affect a client's case is essential. . Even the most specialized practice will encounter many intersections that need to be addressed either by the bankruptcy attorney or a specialist in the respective field.
When a homeowner files for bankruptcy either under Chapter 7 or Chapter 13, the Automatic Stay goes into effect and stops all foreclosure proceedings. The foreclosure sale will be delayed unless the foreclosure notice has already been filed or the creditor files a motion with the bankruptcy court to lift the Automatic Stay.
During the course of the initial interview, a well drafted bankruptcy worksheet or questionnaire will include questions regarding personal injury and worker's compensation claims. A concern among many personal injury plaintiffs is whether a tortfeasor may seek to avoid liability by filing for bankruptcy. A tortfeasor may not discharge a financial obligation incurred as a result of an intentional tort such as assault, battery, false imprisonment, libel, and slander or drunk driving. Other torts are dischargeable. Tort claims are considered unsecured debts and generally receive less protection than secured creditors in the order of priorities. A bankruptcy debtor who is also an injured party in a personal injury case must inform his or her bankruptcy attorney of the existence of a claim. The failure to disclose a pending personal injury claim is considered a crime. When the bankruptcy petition is filed, the trustee assumes control over the personal injury matter and has the authority to settle or litigate the case.
After the debtor files for bankruptcy, any real property the debtor owns is now part of the bankruptcy estate and under the control of the trustee. A debtor does not have the authority to sell or refinance any real property without the approval of the bankruptcy court.
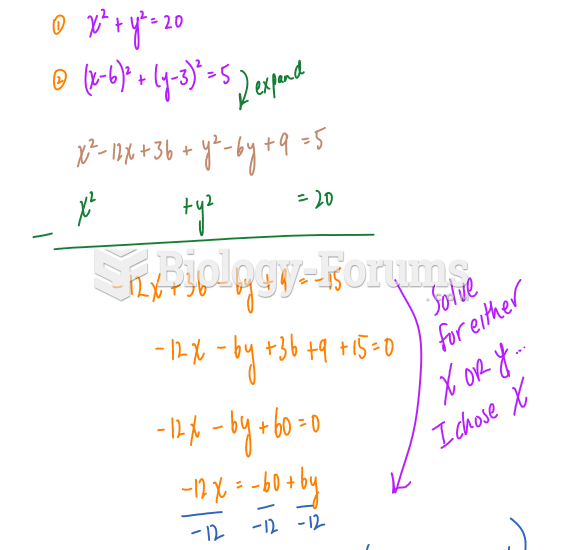
Answer to Question 2
crime