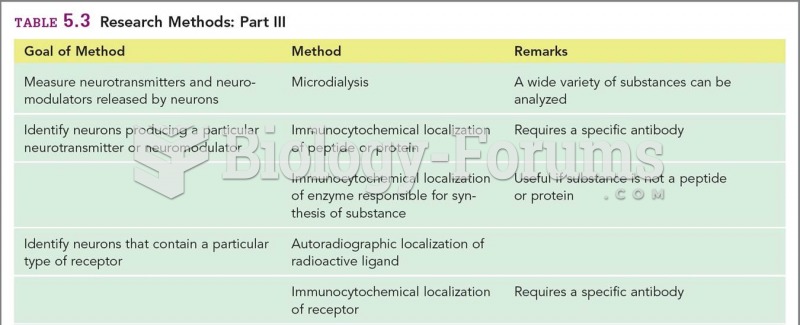
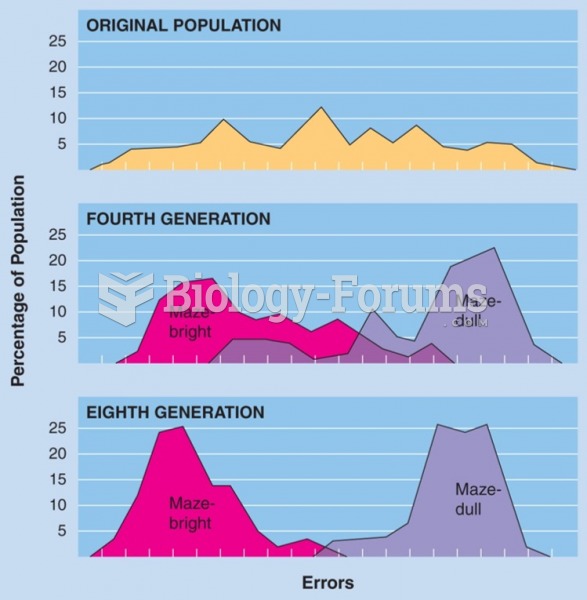
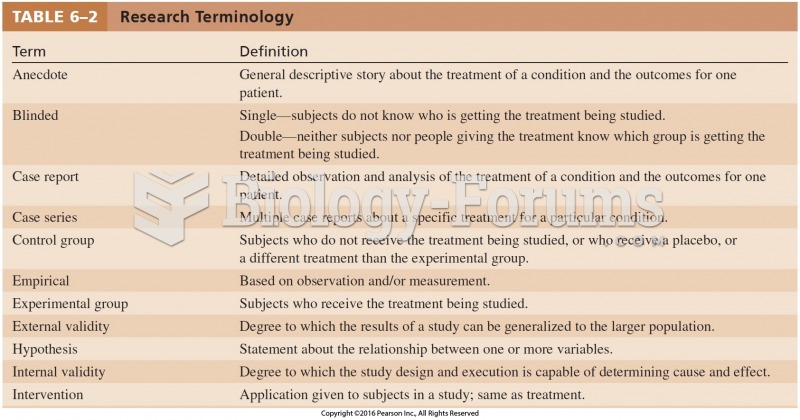
Data snooping is
A) referring to data or research that has not been published.
B) changing the hypothesis of a study after the data have been collected and analyzed.
C) used most often in large scale, lower-constraint research when clues to potential relationships between variables may be buried in the mass of data.
D) used to control confounding variables in experimental research.
Question 2
STUDY: A major airline wants to know if pilots make significantly more errors and more serious errors when they are under a particular stress (e.g., if their airplane is hijacked while in flight).
The airline also wants to know if pilots' years of experience is a factor. The following research is set up. A 767 flight simulator is used. All of the pilot's behavior is monitored, so that the number of errors made by the pilot can be easily read off the computer record. The seriousness of each error is judged later by master pilots using a 25-point scale (interval) of seriousness. The participants are jetliner pilots with experience ranging from 1 to 20 years of commercial piloting. The participants are randomly assigned to two conditions, and the years of experience are the same for both groups.
All pilots simulate take-off from New York, a two-and-a-half hour flight at 32,000 feet cruising altitude, and a landing at Miami. The pilots are told that their job rating depends on how well they handle this simulated flight, and it is impressed on them that they are to do everything as if this were a real flight. In the experimental condition, two masked passengers break into the cockpit 45 minutes into the flight and, aiming guns at the pilots, demand to be taken to Miami for refueling, a payment of a million dollars, and then, flown to Cuba. They threaten to kill some of the passengers and then the pilots and themselves if anything goes wrong. The control group has no hijacking and proceeds to Miami without incident.
What type of design is represented in the research described above?
A) correlated-groups design
B) independent-groups design
C) nonparametric design
D) Both B and C