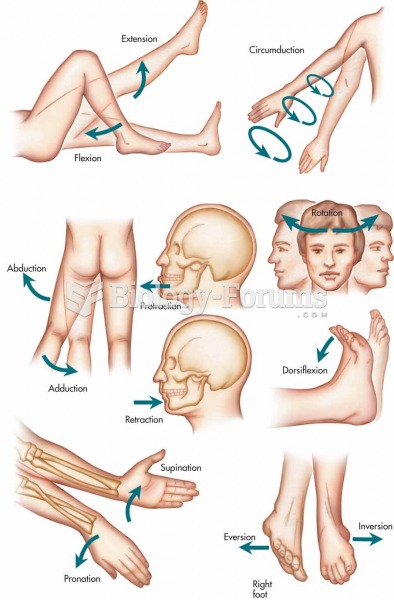
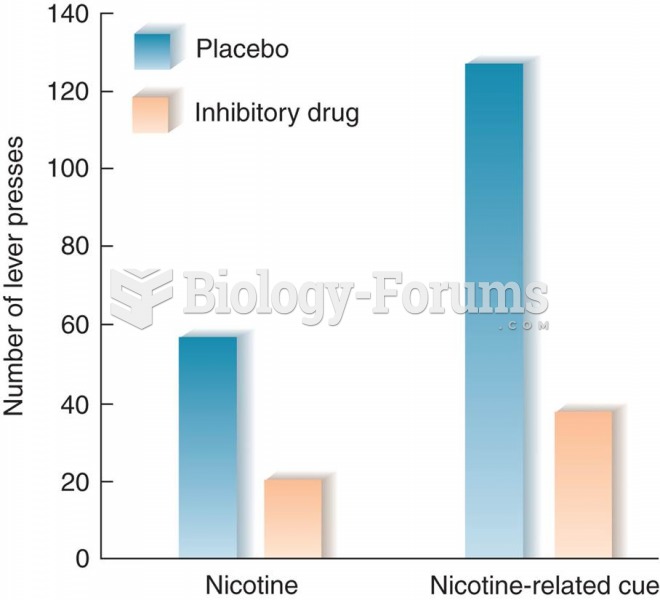
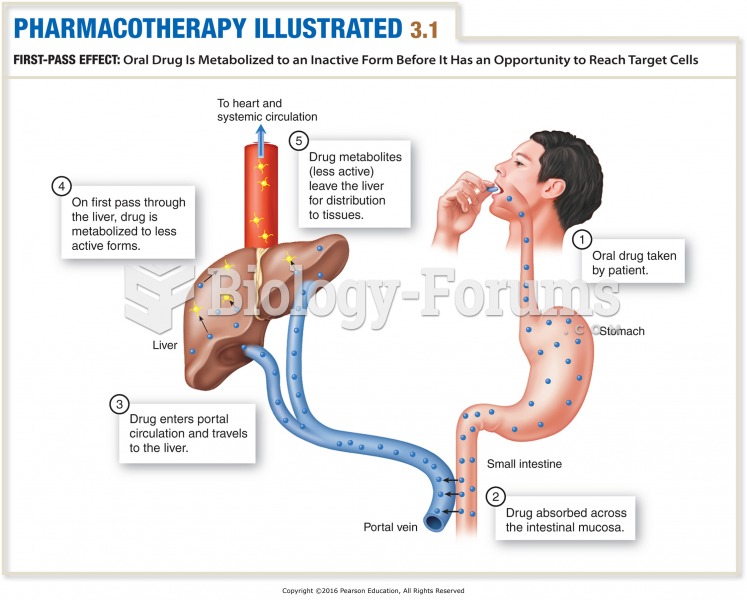
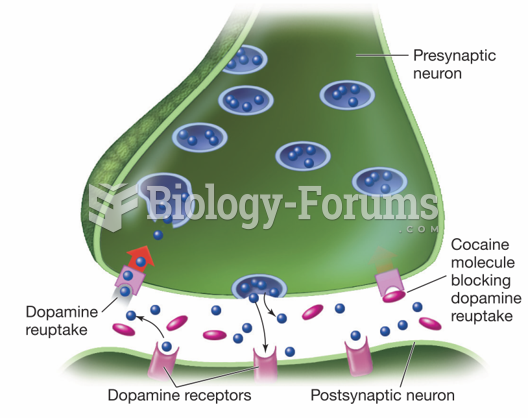
Answer to Question 1
ANS: A nationwide survey of Americans (ages 2575) found different criteria for happiness in various parts of the country. People in the New England states considered physical well-being, autonomy, and not feeling constrained as necessary for subjective well-being. People in western south-central states (Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, and Louisiana) showed a greater concern with personal growth and feelings of cheerfulness and happiness as criteria for subjective well-being. Those in eastern south-central states (Kentucky, Tennessee, Mississippi, and Alabama) focused more on social responsibility and contributing to the welfare and well-being of others as necessary for their own feelings of happiness.
Other research found that subjective well-being was highest in the west coast and mountain states, moderately high in the east coast states, and lowest in the midwestern and southern states. Overall, happiness was significantly related to higher income, higher level of education, and greater tolerance for the views of other people.
A study conducted in regions of Germany over a 24-year period found that as people aged, the life satisfaction of those living in affluent areas remained higher than those living in less affluent regions.
Answer to Question 2
ANS: In Seligman's initial experiments, dogs were harnessed and exposed to painful, though not physically harmful, electric shock. There was no action the dogs could take to escape or avoid the shock. After a series of shocks, the dogs were placed in a two-compartment shuttle box. As in the first experiment Seligman witnessed, a shock was administered through the floor of the compartment. The behavior of these dogs was compared with that of a control group of dogs that had not been exposed to the first electric shocks.
When the dogs in the control group were placed in the box and given the shock through the floor, they raced about the compartment until they accidentally leaped the barrier into the safe compartment. On succeeding trials, they jumped the barrier more quickly each time, having learned that this was the way to escape. The dogs in the experimental group, who had received electric shocks before being placed in the shuttle box, behaved differently. After getting the shock through the compartment floor, they raced around for about 30 seconds and then gave up, dropping to the floor and whimpering. They never learned to escape, not even when experimenters tried to entice them over the barrier with food. These dogs had given up; they had become passive and helpless and would make no attempt to change their situation.
On seeing the results, the experimenters were baffled, but Seligman thought he had a clue. He suggested that perhaps during the first part of the experiment the dogs had learned that they were helpless to change their situation. When the tone sounded, there was nothing they could do to avoid the paired shock. Why even try? This learned reaction apparently generalized to the second part of the experiment, even though a means of escape was available. Seligman wrote, I was stunned by the implications. If dogs could learn something as complex as the futility of their actions, here was an analogy to human helplessness, one that could be studied in the laboratory. Helplessness was all around usfrom the urban poor to the newborn child to the despondent patient with his face to the wall. Was this a laboratory model of human helplessness, one that could be used to understand how it comes about, how to cure it, how to prevent it, what drugs worked on it, and who was particularly vulnerable to it?