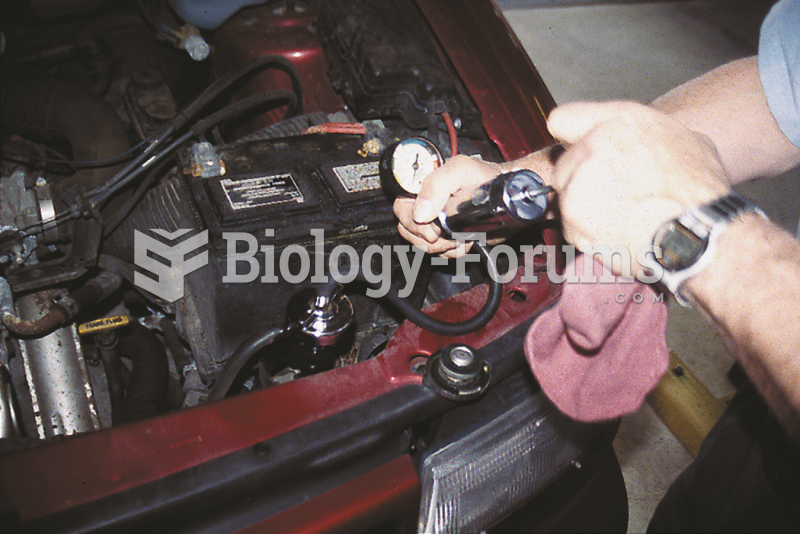
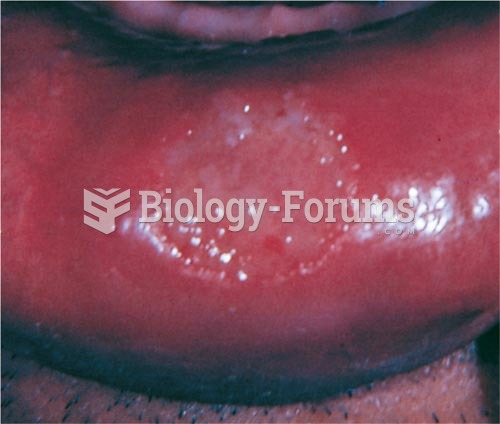
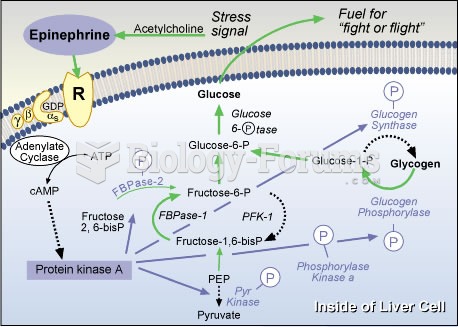
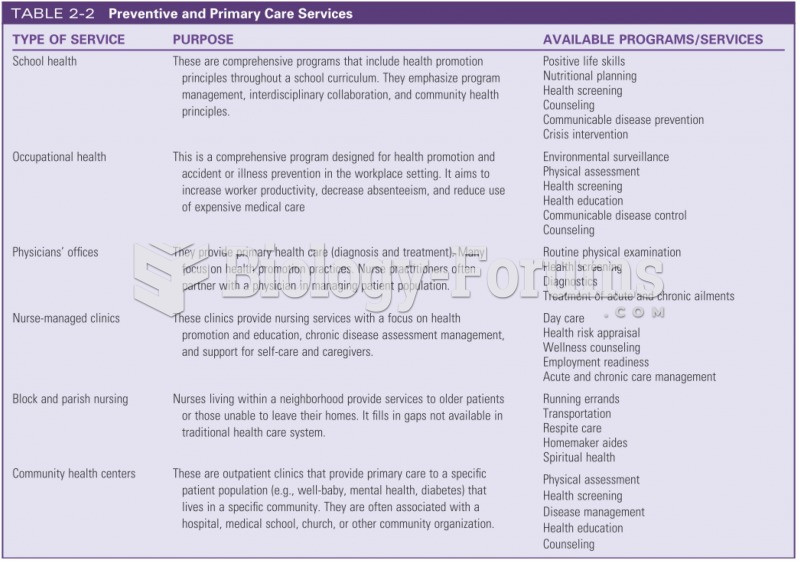
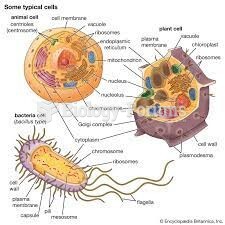
Answer to Question 1
The Equal Pay Act of 1963 is considered by many to be the starting point of the Equal
Employment Opportunity movement in the United States. This law was passed as an amendment
to the 1938 Fair Labor Standards Act. The amendment requires that men and women in an
organization performing basically equal work receive equal pay. Although this law was passed in
1963, equal pay is still the subject of numerous lawsuits today.
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 continued to emphasize equality in personnel policies.
The law applies to all employers with 15 or more employees. Title VII prohibits employment
discrimination based on race, color, sex, religion, and national origin. Those employers that have
less than 15 employees may be subject to state regulations.
The Age Discrimination in Employment Act was passed in 1967 . This law prohibits employers
from discriminating on the basis of age against 40 years old or older. This law impacts all
employers of 20 or more employees and all unions with 25 or more members.
The Vocational Rehabilitation Act was enacted in 1973 and bars discrimination against
otherwise qualified people with disabilities.
The Pregnancy Discrimination Act was enacted in 1978 and prohibits discrimination against
pregnant women.
The American with Disabilities Act was enacted in 1990 . Although this Act was similar to the
Vocational Rehabilitation Act of 1963 the terminology used is somewhat different. The
American with Disabilities Act (ADA) also has broader application. The ADA applies to most
employers and the Vocational Rehabilitation Act applied on to federal contractors and sub-
contractors. Specifically the ADA prohibits workplace discrimination against people with
disabilities.
Answer to Question 2
b