|
|
|
The U.S. Pharmacopeia Medication Errors Reporting Program states that approximately 50% of all medication errors involve insulin.
Medications that are definitely not safe to take when breastfeeding include radioactive drugs, antimetabolites, some cancer (chemotherapy) agents, bromocriptine, ergotamine, methotrexate, and cyclosporine.
Never take aspirin without food because it is likely to irritate your stomach. Never give aspirin to children under age 12. Overdoses of aspirin have the potential to cause deafness.
Though methadone is often used to treat dependency on other opioids, the drug itself can be abused. Crushing or snorting methadone can achieve the opiate "rush" desired by addicts. Improper use such as these can lead to a dangerous dependency on methadone. This drug now accounts for nearly one-third of opioid-related deaths.
The first monoclonal antibodies were made exclusively from mouse cells. Some are now fully human, which means they are likely to be safer and may be more effective than older monoclonal antibodies.
 The terrorist attack of September 11, 2001, is surely a defining event for the cohorts who experienc
The terrorist attack of September 11, 2001, is surely a defining event for the cohorts who experienc
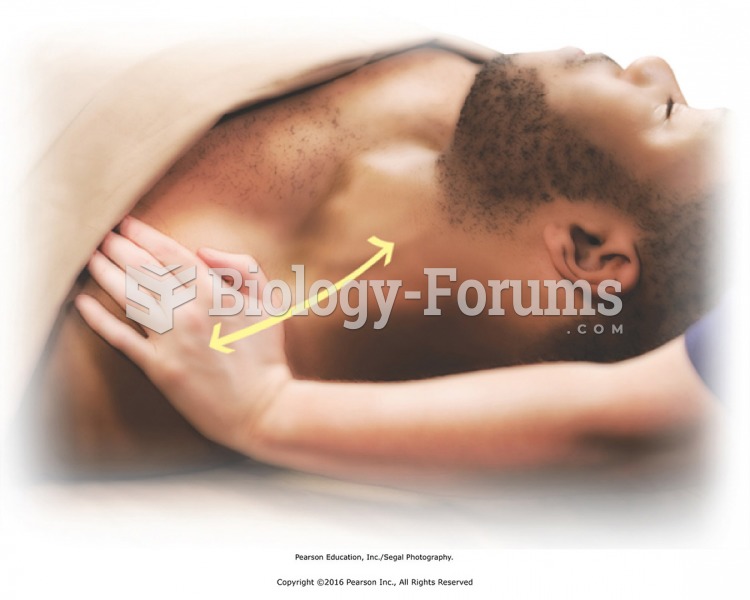
 Cross-fiber friction to the paraspinal muscles. Friction is created by moving the more superficial ...
Cross-fiber friction to the paraspinal muscles. Friction is created by moving the more superficial ...
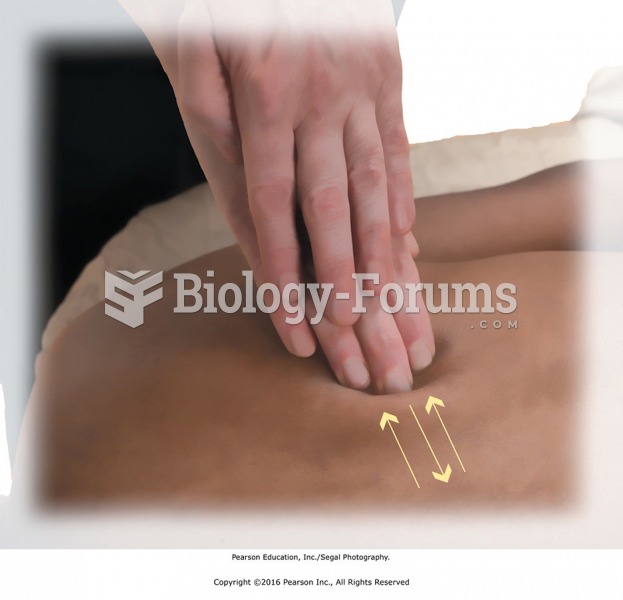
 Direct thumb pressure along the tibialis anterior. Start at proximal end, moving about 1 inch at a ...
Direct thumb pressure along the tibialis anterior. Start at proximal end, moving about 1 inch at a ...