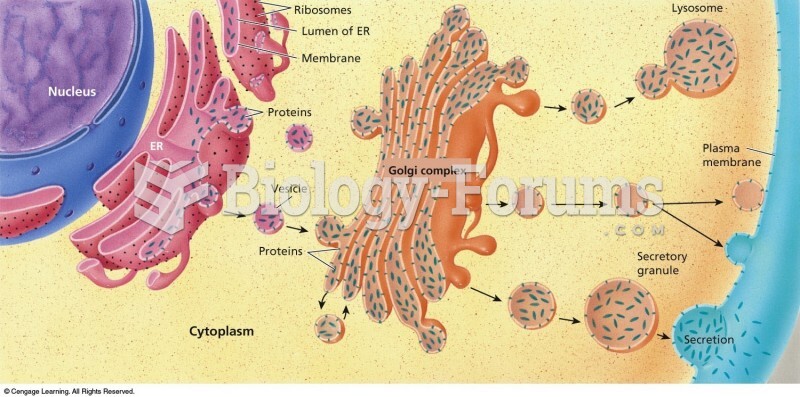
|
|
|
Did you know?
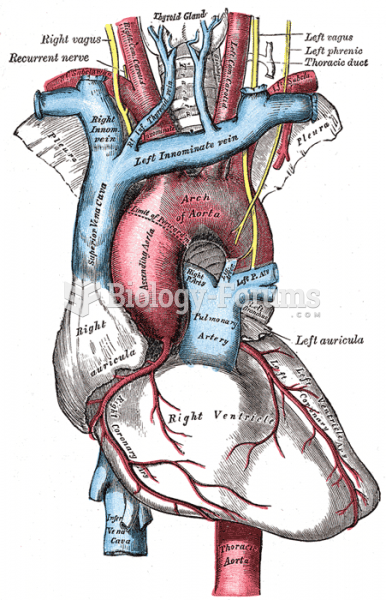
When blood is exposed to air, it clots. Heparin allows the blood to come in direct contact with air without clotting.
Did you know?
There are approximately 3 million unintended pregnancies in the United States each year.
Did you know?
Atropine, along with scopolamine and hyoscyamine, is found in the Datura stramonium plant, which gives hallucinogenic effects and is also known as locoweed.
Did you know?
Eat fiber! A diet high in fiber can help lower cholesterol levels by as much as 10%.
Did you know?
The immune system needs 9.5 hours of sleep in total darkness to recharge completely.