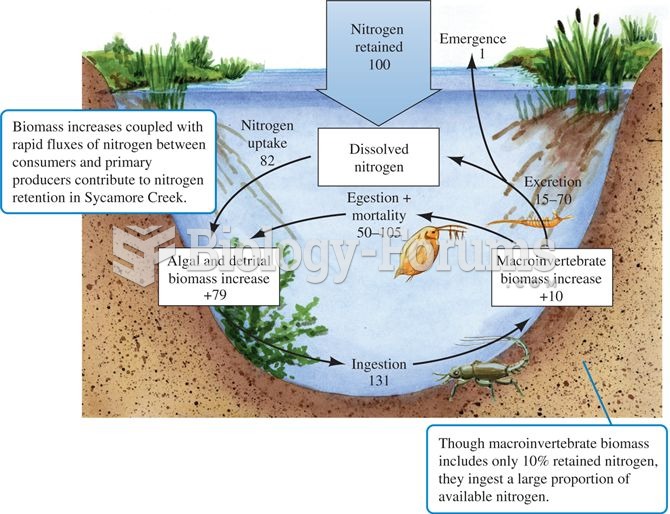
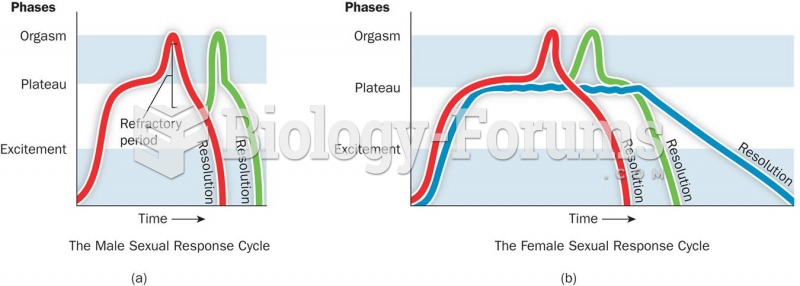
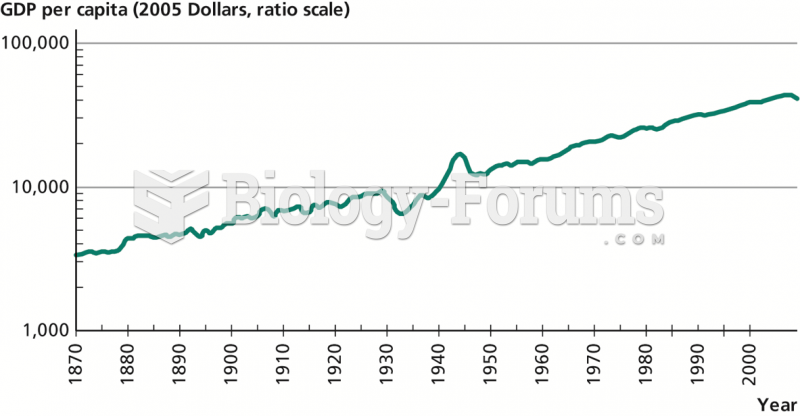
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Pregnant women usually experience a heightened sense of smell beginning late in the first trimester. Some experts call this the body's way of protecting a pregnant woman from foods that are unsafe for the fetus.
Did you know?
The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen in water (H2O) is 2:1.
Did you know?
The average human gut is home to perhaps 500 to 1,000 different species of bacteria.
Did you know?
Thyroid conditions may make getting pregnant impossible.
Did you know?
If all the neurons in the human body were lined up, they would stretch more than 600 miles.