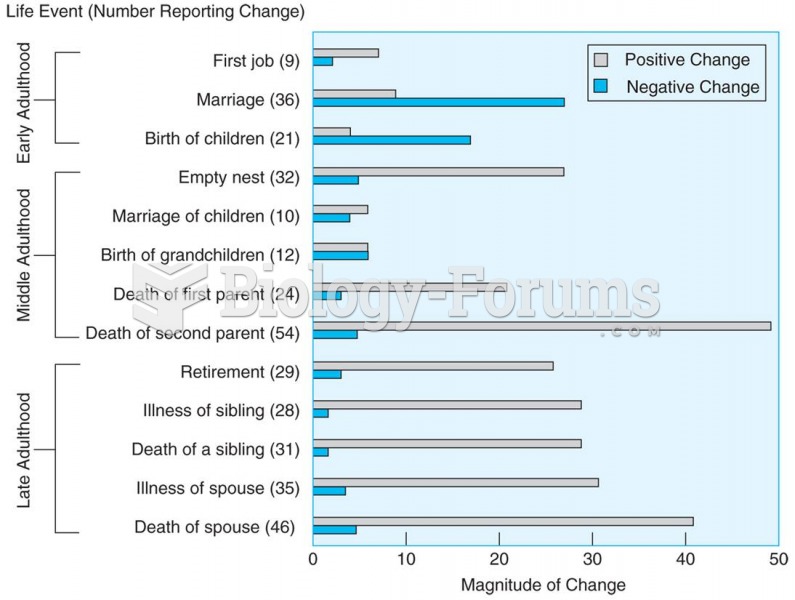
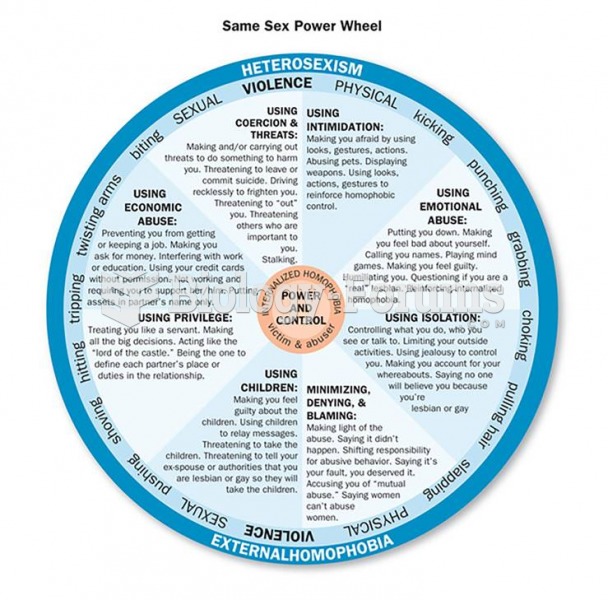
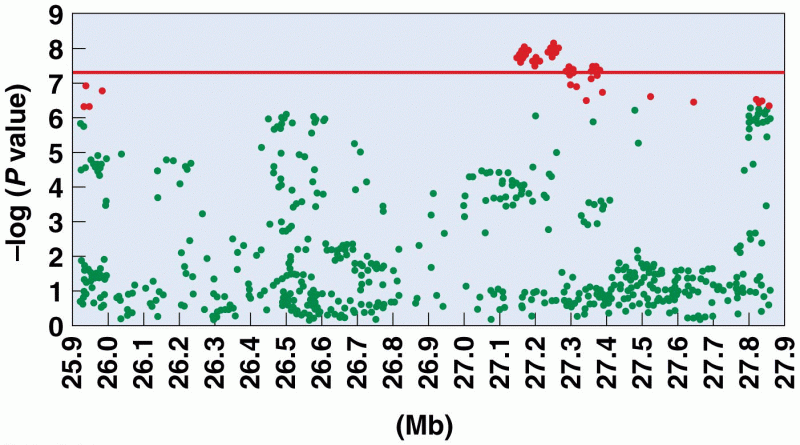
|
|
|
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.
Illness; diuretics; laxative abuse; hot weather; exercise; sweating; caffeine; alcoholic beverages; starvation diets; inadequate carbohydrate consumption; and diets high in protein, salt, or fiber can cause people to become dehydrated.
People often find it difficult to accept the idea that bacteria can be beneficial and improve health. Lactic acid bacteria are good, and when eaten, these bacteria improve health and increase longevity. These bacteria included in foods such as yogurt.
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.
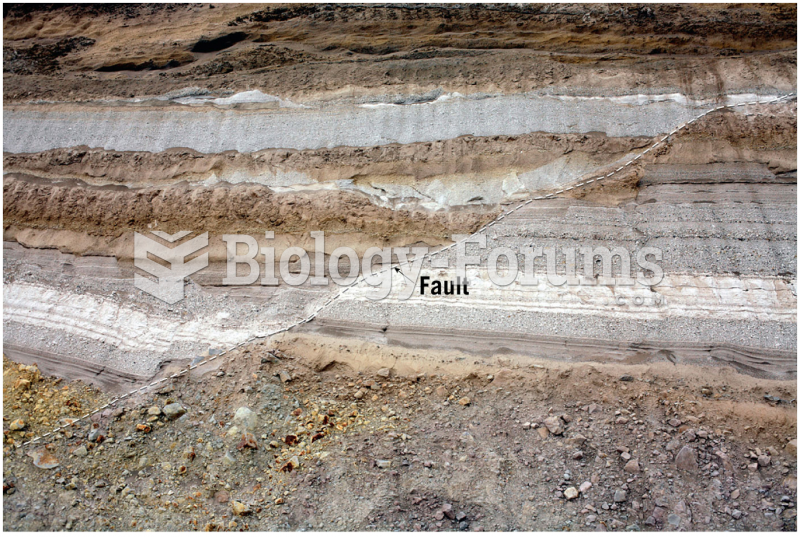
As the western states of America were settled, pioneers often had to drink rancid water from ponds and other sources. This often resulted in chronic diarrhea, causing many cases of dehydration and death that could have been avoided if clean water had been available.