|
|
|
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.
Nearly all drugs pass into human breast milk. How often a drug is taken influences the amount of drug that will pass into the milk. Medications taken 30 to 60 minutes before breastfeeding are likely to be at peak blood levels when the baby is nursing.
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.
Calcitonin is a naturally occurring hormone. In women who are at least 5 years beyond menopause, it slows bone loss and increases spinal bone density.
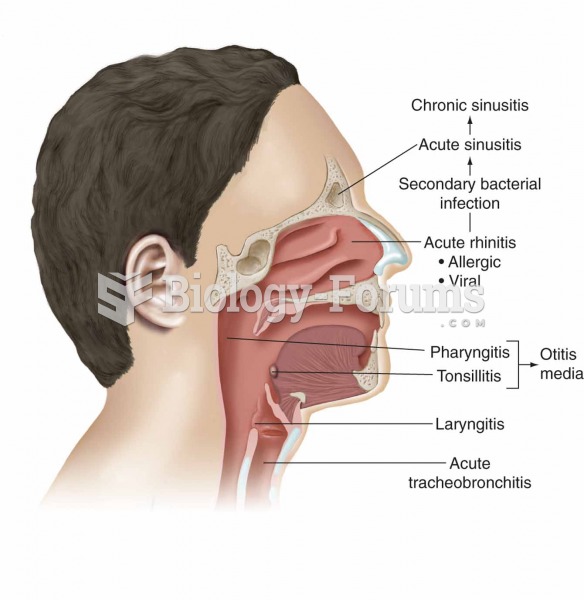
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.