|
|
|
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%.
More than 50% of American adults have oral herpes, which is commonly known as "cold sores" or "fever blisters." The herpes virus can be active on the skin surface without showing any signs or causing any symptoms.
The training of an anesthesiologist typically requires four years of college, 4 years of medical school, 1 year of internship, and 3 years of residency.
According to the Migraine Research Foundation, migraines are the third most prevalent illness in the world. Women are most affected (18%), followed by children of both sexes (10%), and men (6%).
Normal urine is sterile. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It is free of bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
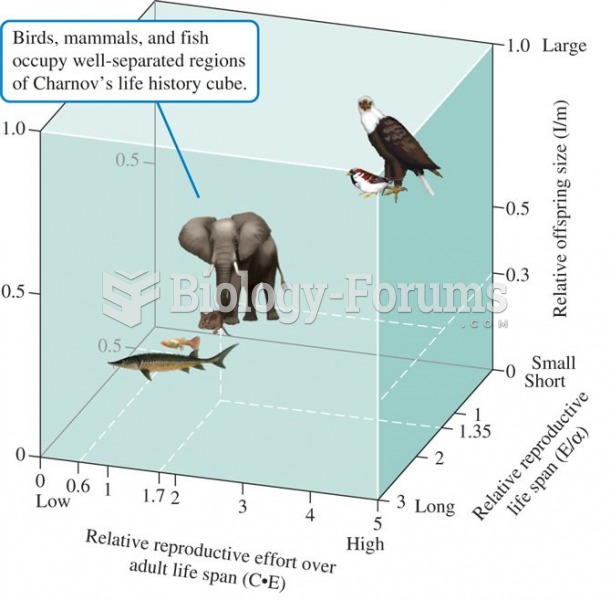 Life-history cube, a classification of fish, mammals, and altricial birds based on three dimensionle
Life-history cube, a classification of fish, mammals, and altricial birds based on three dimensionle
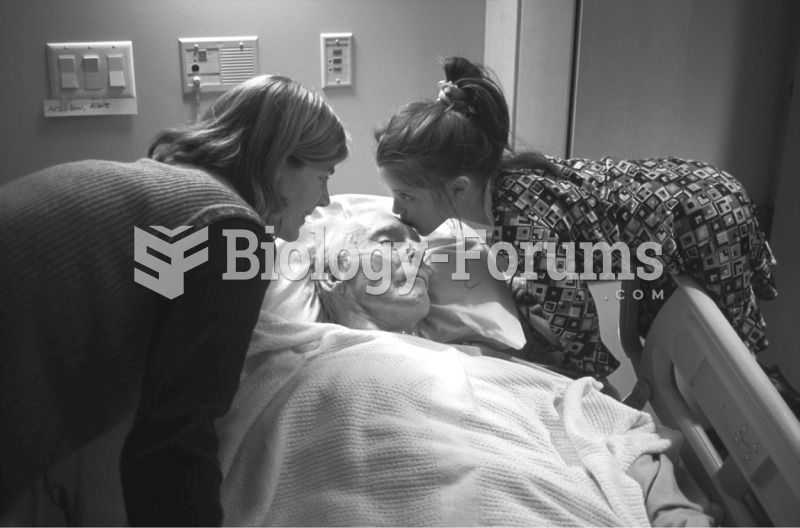
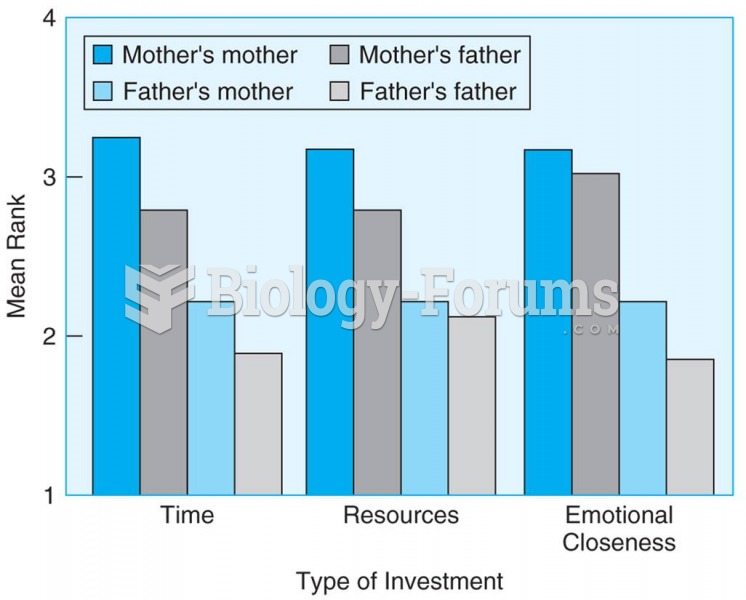 Students rated their grandparents on a scale from 1 to 4 based on emotional closeness, time spent ...
Students rated their grandparents on a scale from 1 to 4 based on emotional closeness, time spent ...