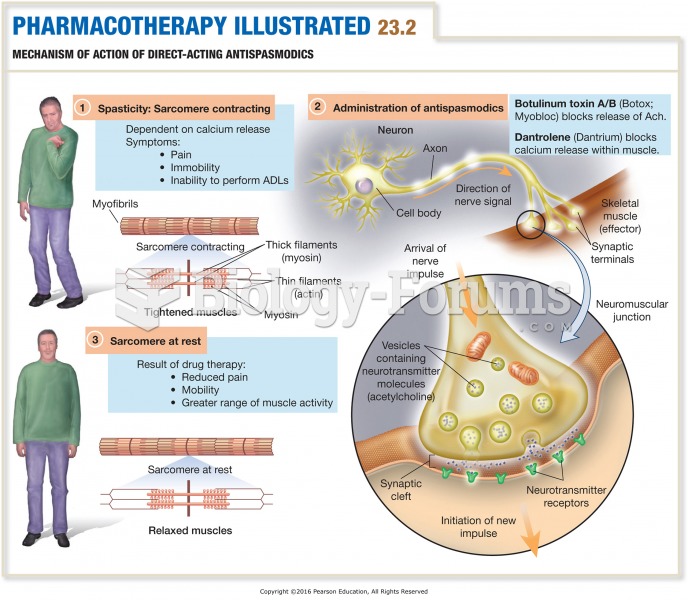
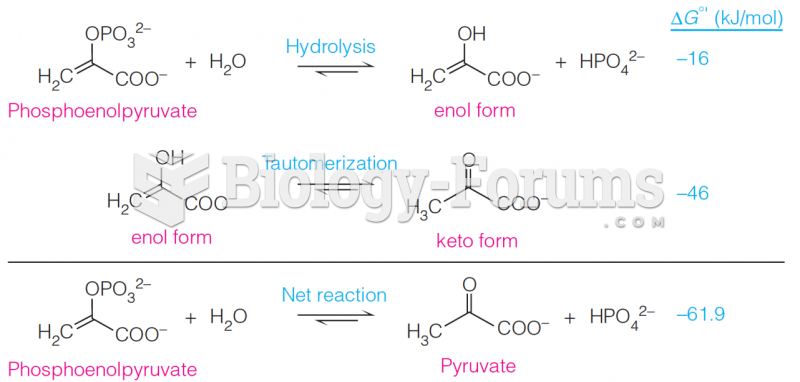
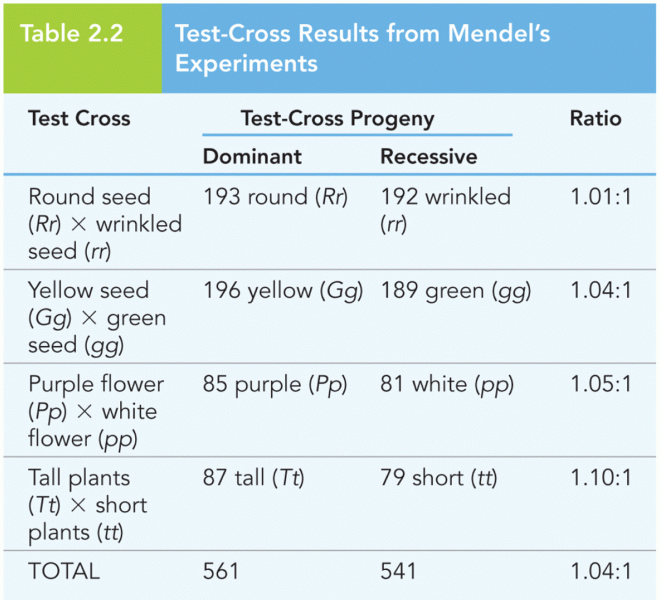
|
|
|
Eating carrots will improve your eyesight. Carrots are high in vitamin A (retinol), which is essential for good vision. It can also be found in milk, cheese, egg yolks, and liver.
Asthma occurs in one in 11 children and in one in 12 adults. African Americans and Latinos have a higher risk for developing asthma than other groups.
In the ancient and medieval periods, dysentery killed about ? of all babies before they reach 12 months of age. The disease was transferred through contaminated drinking water, because there was no way to adequately dispose of sewage, which contaminated the water.
Giardia is one of the most common intestinal parasites worldwide, and infects up to 20% of the world population, mostly in poorer countries with inadequate sanitation. Infections are most common in children, though chronic Giardia is more common in adults.
Drug abusers experience the following scenario: The pleasure given by their drug (or drugs) of choice is so strong that it is difficult to eradicate even after years of staying away from the substances involved. Certain triggers may cause a drug abuser to relapse. Research shows that long-term drug abuse results in significant changes in brain function that persist long after an individual stops using drugs. It is most important to realize that the same is true of not just illegal substances but alcohol and tobacco as well.