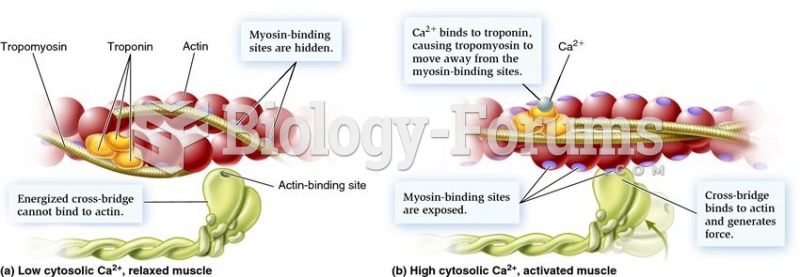
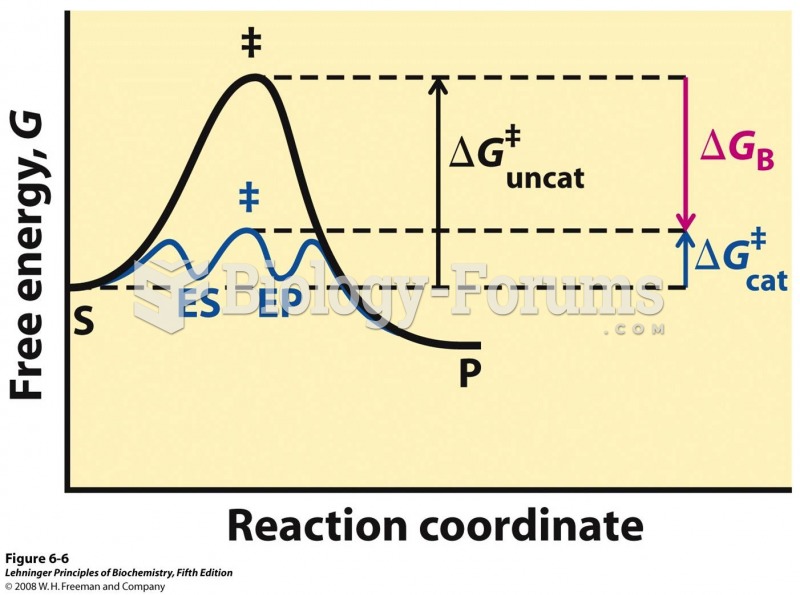
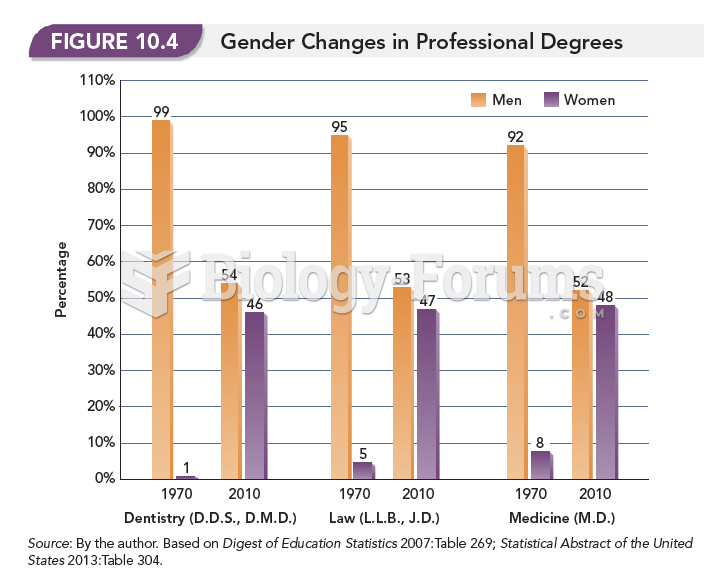
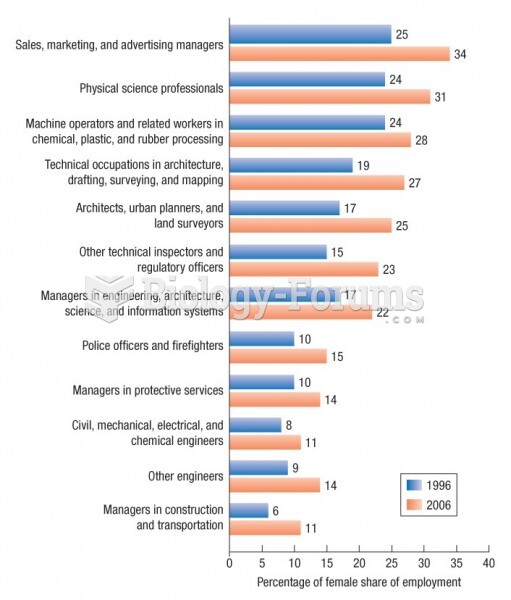
|
|
|
Astigmatism is the most common vision problem. It may accompany nearsightedness or farsightedness. It is usually caused by an irregularly shaped cornea, but sometimes it is the result of an irregularly shaped lens. Either type can be corrected by eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery.
The first monoclonal antibodies were made exclusively from mouse cells. Some are now fully human, which means they are likely to be safer and may be more effective than older monoclonal antibodies.
The most common childhood diseases include croup, chickenpox, ear infections, flu, pneumonia, ringworm, respiratory syncytial virus, scabies, head lice, and asthma.
In inpatient settings, adverse drug events account for an estimated one in three of all hospital adverse events. They affect approximately 2 million hospital stays every year, and prolong hospital stays by between one and five days.
Hyperthyroidism leads to an increased rate of metabolism and affects about 1% of women but only 0.1% of men. For most people, this increased metabolic rate causes the thyroid gland to become enlarged (known as a goiter).