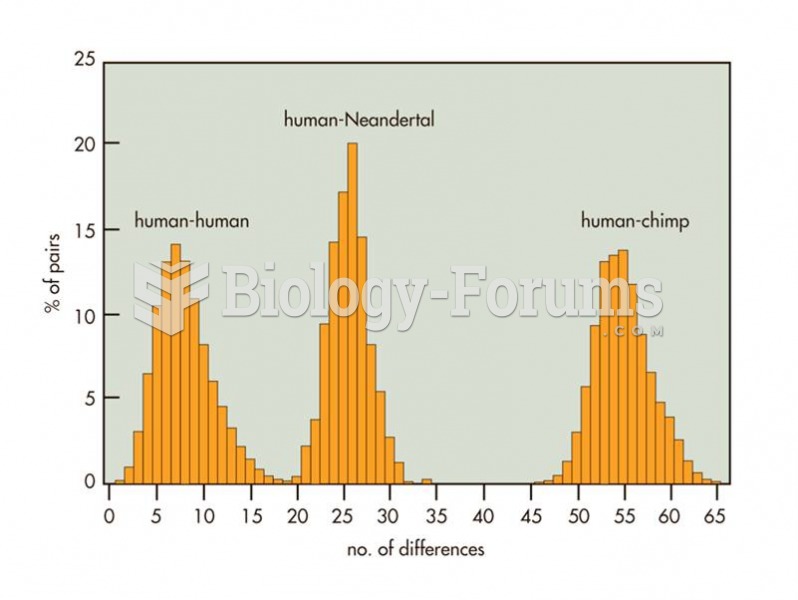
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all women age 65 years of age or older should be screened with bone densitometry.
Did you know?
Patients should never assume they are being given the appropriate drugs. They should make sure they know which drugs are being prescribed, and always double-check that the drugs received match the prescription.
Did you know?
Oliver Wendell Holmes is credited with introducing the words "anesthesia" and "anesthetic" into the English language in 1846.
Did you know?
Vaccines prevent between 2.5 and 4 million deaths every year.
Did you know?
All adverse reactions are commonly charted in red ink in the patient's record and usually are noted on the front of the chart. Failure to follow correct documentation procedures may result in malpractice lawsuits.
 Taking an interesting course can help keep your brain active. These seniors are taking a class in ...
Taking an interesting course can help keep your brain active. These seniors are taking a class in ...
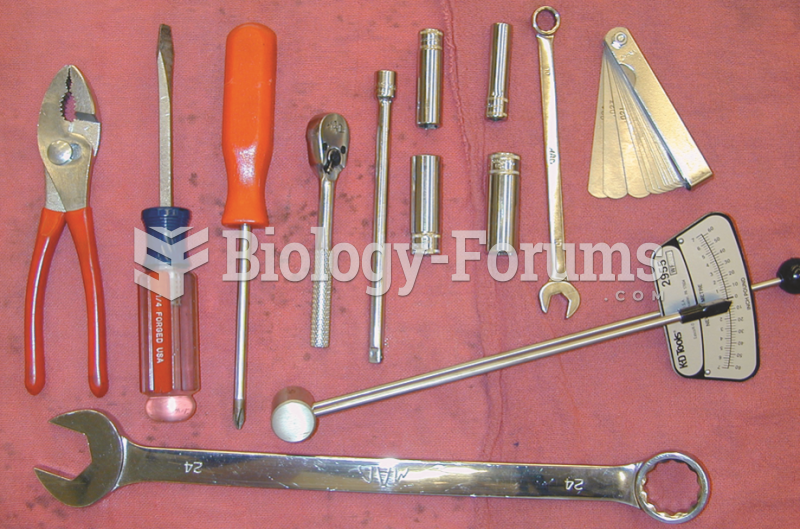 The tools necessary to adjust the valves on an engine with adjustable rocker arms include basic hand ...
The tools necessary to adjust the valves on an engine with adjustable rocker arms include basic hand ...