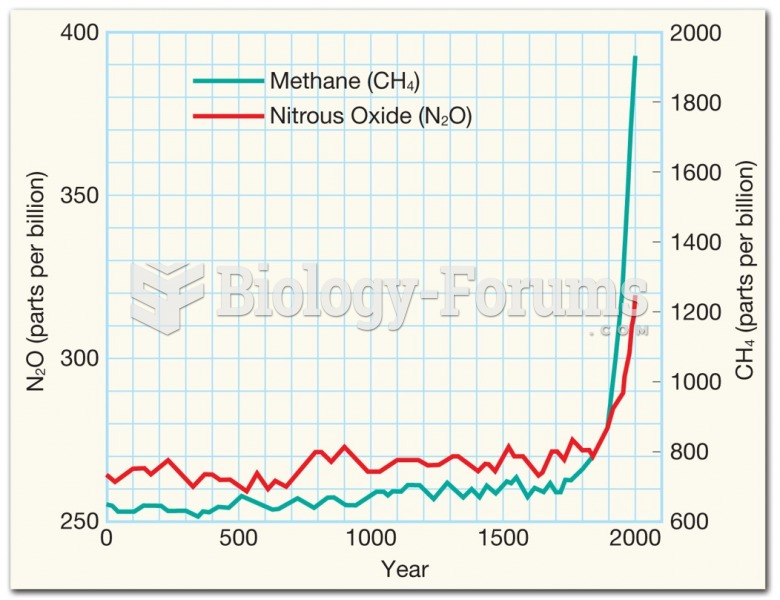
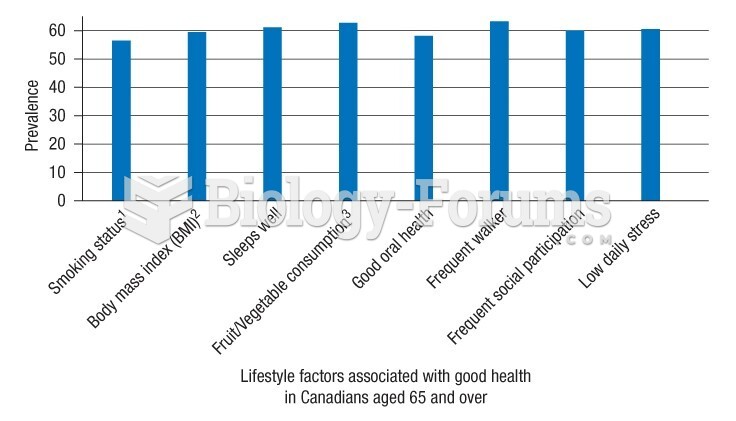
|
|
|
People who have myopia, or nearsightedness, are not able to see objects at a distance but only up close. It occurs when the cornea is either curved too steeply, the eye is too long, or both. This condition is progressive and worsens with time. More than 100 million people in the United States are nearsighted, but only 20% of those are born with the condition. Diet, eye exercise, drug therapy, and corrective lenses can all help manage nearsightedness.
According to the CDC, approximately 31.7% of the U.S. population has high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad cholesterol" levels.
The Romans did not use numerals to indicate fractions but instead used words to indicate parts of a whole.
Essential fatty acids have been shown to be effective against ulcers, asthma, dental cavities, and skin disorders such as acne.
Colchicine is a highly poisonous alkaloid originally extracted from a type of saffron plant that is used mainly to treat gout.
 Alligators are apex predators capable of killing large terrestrial prey. This large AAmerican alliga
Alligators are apex predators capable of killing large terrestrial prey. This large AAmerican alliga
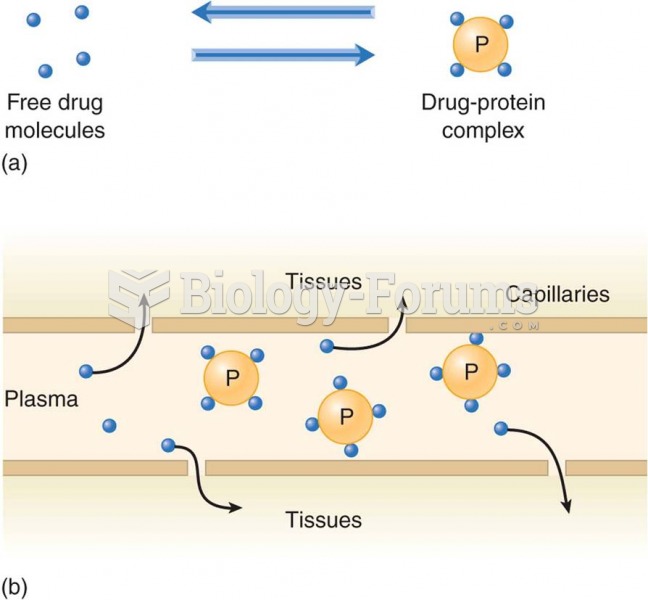 Plasma protein binding and drug availability: (a) drug exists in a free state or bound to plasma pro
Plasma protein binding and drug availability: (a) drug exists in a free state or bound to plasma pro