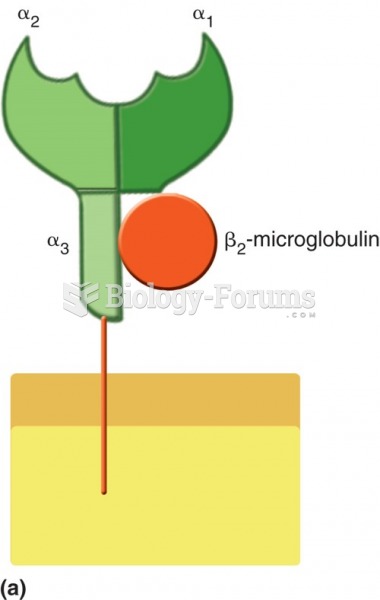
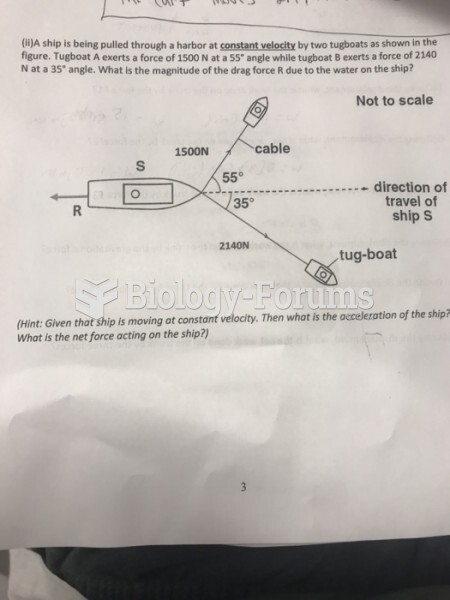
|
|
|
A recent study has found that following a diet rich in berries may slow down the aging process of the brain. This diet apparently helps to keep dopamine levels much higher than are seen in normal individuals who do not eat berries as a regular part of their diet as they enter their later years.
Patients who cannot swallow may receive nutrition via a parenteral route—usually, a catheter is inserted through the chest into a large vein going into the heart.
More than 2,500 barbiturates have been synthesized. At the height of their popularity, about 50 were marketed for human use.
According to the CDC, approximately 31.7% of the U.S. population has high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad cholesterol" levels.
About 3% of all pregnant women will give birth to twins, which is an increase in rate of nearly 60% since the early 1980s.
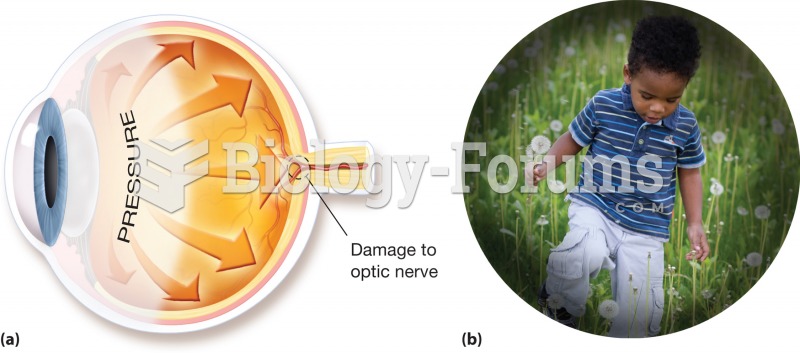 Glaucoma. (a) A buildup of pressure within the eye cavities, often caused by a blockage of vessels t
Glaucoma. (a) A buildup of pressure within the eye cavities, often caused by a blockage of vessels t
 Vision with macular degeneration is experienced with an inability to focus in the center of the visu
Vision with macular degeneration is experienced with an inability to focus in the center of the visu
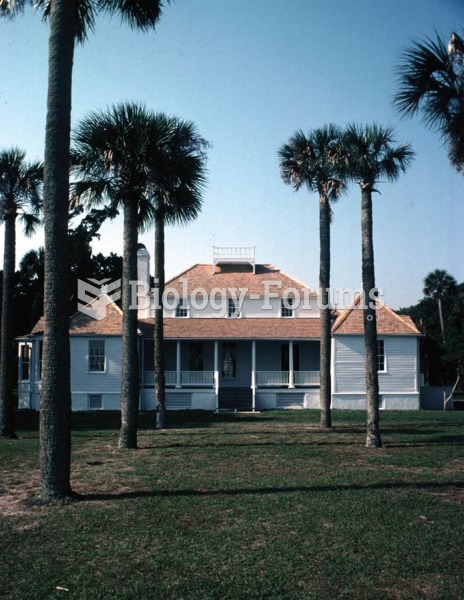 The Kingsley plantation, on Fort George Island in Jacksonville, Florida. Zephaniah Kingsley, the own
The Kingsley plantation, on Fort George Island in Jacksonville, Florida. Zephaniah Kingsley, the own